Page 9 of 11
Drilling Simulator for iPhone and iPod Touch – User Guide
Drilling Simulator for iPad User Guide
Oil & Gas Apps for Mac OS X
Oil & Gas Apps for Mac OS X
A few years ago, we searched for applications in the area of oil and gas for Mac OS X and not found. Then, we develop these applications and we would like to share with friends.
We would like to share our portfolio with very low cost applications to drillers, tool pushers, engineers, chemists, students and other professionals in the petroleum industry. These are productivity tools helpful in drilling of oil wells.
These apps are completely interactive and allow users to define a wide variety of parameters for oil wells and unit system, save data, share them with friends.
These Apps are available on the Mac App Store, only.
Well Control Methods |
Well Control Worksheets |
Kick Tolerance |
Well Control Simulator for iPhone and iPod Touch 1.4 now available on the App Store: Improvements
Well Control Simulator for iPhone and iPod Touch 1.4
Now available on the App Store
Features:
Well Control Simulator Provides a graphical very useful tool for training of roughnecks, derrickmen, drillers, tool pushers, drilling engineers and students in the well control procedures.
– Interactive System: no pre-set methods;
– Ability to apply methods: Driller’s method, wait and weight, dynamic volumetric and static volumetric (lubricate and bleed);
– Capacities and Volumes;
– Hydraulics and Hydrostatics and critical pressures calculations;
– Behavior of the kick;
– Applied with subsea stack and surface stack;
Kick Model:
The model assumes that the kick starts as a single bubble and migrates upward as a single bubble from the bottom to the surface.
Notes:
- For simulation of drilling and kick detection, use another app “Drilling Simulator“.
- For simulation of leak-off test, use another app “Leak-Off Test Simulator“;
- For methods to control, use another app “Well Control Methods“;
- For kick tolerance calculations, use another app “Kick Tolerance“;
- For hydraulic calculations, use another app “Drilling Hydraulics“;
New in this update 1.4:
- Improved Stability;
- Improved Well Configuration;
- Improved the work with data files;
- Added button to reset kick
- Fix bug to reset fracture
New screenshots
Other screenshots
Driller’s Method:
Wait and Weight Method:
Drilling Simulator for iPhone and iPod Touch 1.5 now available on the App Store: Improvements
Drilling Simulator for iPhone and iPod Touch 1.5
Now available
Features:
1) Panel with the following parameters: pump pressure, mud pump speed, strokes totalizer, flow rate, mud weight, bit depth, rotary speed, hookload and weight on the bit;
2) Instruments with pointers to the parameters: pump pressure, hookload, weight on the bit and rotary torque;
3) Geolograph with parameters: drillpipe pressure, choke pressure, active volume, hookload, weight on the bit, length drilled, flow in, flow out, percent of flow, rotary torque, rotary speed and drilling rate.
4) Panel with alarms: pump failure, vol high, flow high, bop failure, bop status and choke status;
5) Toolbar with buttons: Well Config, Circulation Options, Set Alarms, Graph Limits, X-times faster, Pause/Continue, Restart, Send by email, about;
6) set drillstring with drillpipe1, drillpipe2, heavy-weight, drillcollar1 and drillcollar2;
7) Select floating rig or land rig;
8) Select unit systems: International, field1 (imperial) and field2 (mix);
9) set fluid parameters: mud weight, plastic viscosity, yield point and initial gel;
10) Select rheological models: Power or Bingham;
11) Set gradients: absorption, fracture and temperature;
12) Set jet nozzles or fixed TFA;
13) Set choke parameters and BOP test pressure;
14) Set Surface circulation volume;
15) Set surface circulation equipments (mud pump and lines);
16) Set four formations to drilling (height, pore gradient, fluid density and sof/hard);
17) Save configuration to data files and share by iCloud;
18) Select circulation options: drillpipe -> Riser, Kill -> Riser, and Close BOP;
19) Set alarms: pit gain, flow rate out, max pump pressure and max pump power;
20) Register the kill line losses and pump pressure at the kill speed;
21) show the well with drillstring and the drillbit on rotating;
22) Show schematic of well with drillstring, kick and neutral point (%);
23) Adjust pump speed, weight on the bit and rotary speed to drilling until kick detection;
24) Shut-in the well using hard method;
25) Register shut-in drillpipe pressure (SIDPP) and choke pressure (SICP) and gain volume;
26) behavior of the kick: keeping the well closed and keeping the well opened;
27) Simulations: Drilling, Kick detection, Shut-In, Underground Blowout at shoe and blowout with failure of bop;
28) Capacities and Volumes calculations;
29) Hydrostatic and critical pressures calculations;
30) Hydraulics calculations;
Note: This Drilling Simulator NOT allows to control the well after the kick detection and shut-in. The simulation ends after the simulations of underground blowout and blowout to surface.
Notes:
- For well control simulations, use another app “Well Control Simulator“.
- For simulation of leak-off test, use another app “Leak-Off Test Simulator“;
- For methods to control, use another app “Well Control Methods“;
- For kick tolerance calculations, use another app “Kick Tolerance“;
- For hydraulic calculations, use another app “Drilling Hydraulics“;
New in this update:
- Improved Stability
- Improved Well Configuration
- Improved the work with data files
- Added reset buttons for reset kick, fracture and graph
Other Screenshots (Current versions)
Screenshot on iPhone 4
The following screenshots were taken on iPod 5th gen (iPhone 5 larger display)
Drill, detect kick, close the well and wait for stabilization of the pressures:
Screenshot in real size on iPod Touch 5th gen (640×1136)
Import by iCloud from the app “Well Control Simulator” to control:
Well Control Simulator for iPhone (new version 1.2)
Well Control for iPad (new version 1.2)
Other Screenshots of the Drilling Simulator
Updates to All Apps for iPhone, iPod Touch and iPad submitted to the App Store – Send by Email / Open in
All Apps for iPhone, iPod Touch and iPad
*** Now Available ***
New in these updates:
– Send data file by email;
– Open in… (on Mail App and file managers apps)
– Backup and Restore data files with iTunes File Sharing.
On iPhone and iPod Touch


On iPad


iTunes File Sharing

Leak-Off Test Simulator for iPad 1.2 now available on the App Store
Leak-Off Test Simulator for iPad
New in this update:
- – Support for iOS 6;
- – Improved printing and attachments with retina display;
- – Selection of units also per parameter;
- – Ability to import well data from other apps using iCloud;
- – Ability to use the iPad on landscape position on all views;
- – Recalculate DP as necessary to surface automatically with bit on bottom when editing BHA or Well Depth;
- – Revision of the code;
- – Several improvements
This app provides a graphical very useful tool for training of Technicians, Drillers, Toolpushers, Drilling Engineers, Students and others professionals of the oil & gas industry to simulate leak-off test and more: hydraulics, hydrostatic, capacities and volumes, ability to select unit systems: Metric, Si, Imperial and Field (mix), very useful for filling well control worksheets.
About the Leak-off Test on drilling operations:
A test to determine the strength or fracture pressure of the open formation, usually conducted immediately after drilling below a new casing shoe.
Initially, pumping fluid into the borehole results in volumetric compression of the drilling mud column and elastic expansion of the casing string plus rock around the borehole. As the pressure in the borehole increases, the leak-off pressure (LOP) is reached when the relationship between pressure increase and volume of fluid pumped deviates from linear. This occurs when fluid begins to diffuse into the formation at a more rapid rate as the rock begins to dilate. Generally, a LOT is a test that finishes immediately after LOP is reached.
Features:
1) Panel with the following parameters: pump pressure, choke pressure, mud pump speed, strokes totalizer, flow rate, mud weight and volume;
2) Intuitive graphical interface: Instruments with pointers to the parameters: pump pressure, choke pressure and open/close hydraulic choke;
3. Graph Options:
– Pressures Pump / Choke and Volume Pumped versus Pumping Time;
– Pressures Pump/ Choke and Pumping Time versus Volume Pumped;
4) Panel with alarms: pump failure, bop failure and bop status;
5) Toolbar with buttons: Data File, Well Config, Restart, Ranges, Set Alarms, Graph Limits, Pause/Continue, Restart, Set BOP, Send by email, about;
6) Set drillstring with drillpipe1, drillpipe 2, heavy-weight, drillcollar1 and drillcollar2;
7) Select floating rig or land rig;
8) Select unit systems: Metric, SI, field1 (imperial) and field2 (mix);
9) set fluid parameters: mud weight, plastic viscosity, yield point and initial gel;
10) Select rheological models: Power or Bingham;
11) Set gradients: absorption and fracture;
12) Set jet nozzles or fixed TFA;
13) Set choke parameters and BOP test pressure;
14) Vertical or Slant Well Type (KOP, TVD and Measured Depth);
15) Set surface circulation equipments (mud pump and lines);
16) Save configuration to data files;
17) Select circulation options: drillpipe -> riser and drillpipe -> choke, Close/Open (Hard shut-in) the well;
18) Reset alarms: pump failure: max pump speed, max pump pressure and max pump power;
19) Register the pressures at the kill speed ;
20) Show schematic of well with drillstring and riser, casing, liner and open hole;
21) Shut-in the well using hard method;
22) Circulation on slow rate (kill speed);
23) Useful for filling of Standardized Kill Sheets for Well Control;
24) Useful for Filling of Previous Recorded Sheets;
25) Analize of the Choke Line effect in Maximum Choke Pressure;
26) Analize of the Effect of porosity and permeability on absorption curve;
27) Simulation of the Leak-Off Test operation and Graphical Analize of the Leak-Off Test
28) Capacities and Volumes calculations;
29) Hydrostatic and critical pressures calculations;
30) Hydraulics calculations;
Basic Exercise:
1. Close BOP and Choke;
2. Set Mud Pump Speed;
3. Monitor the Choke Pressure;
4. When the pressure deviates from linear, stop the mud pump;
5. Wait until the choke pressure stabilize;
6. Tap on graph to obtain data;
7. Open choke to bleed until choke pressure to zero;
Notes:
1. Set fracture gradient > absorption gradient;
2. The Absorption curve is function of porosity and permeability.
3. Tap with finger and moving it in the graph area to obtain Choke Pressure,
Equivalent Density, Equivalent Gradient, Volume Pumped and Pumping Time.

contact@wellcontrol.com.br
Leak-Off Test Simulator for iPhone and iPod Touch 1.2 now available on the App Store
Leak-Off Test Simulator for iPhone and iPod Touch
New in this update:
- – Support for iOS 6 / and iPhone 5;
- – Improved printing and attachments with retina display;
- – Selection of units also per parameter;
- – Ability to import well data from other apps using iCloud;
- – Recalculate DP as necessary to surface automatically with bit on bottom when editing BHA or Well Depth;
- – Revision of the code;
- – Several improvements
This app provides a graphical very useful tool for training of Technicians, Drillers, Toolpushers, Drilling Engineers, Students and others professionals of the oil & gas industry to simulate leak-off test and more: hydraulics, hydrostatic, capacities and volumes, ability to select unit systems: Metric, Si, Imperial and Field (mix), very useful for filling well control worksheets.
About the Leak-off Test on drilling operations:
A test to determine the strength or fracture pressure of the open formation, usually conducted immediately after drilling below a new casing shoe.
Initially, pumping fluid into the borehole results in volumetric compression of the drilling mud column and elastic expansion of the casing string plus rock around the borehole. As the pressure in the borehole increases, the leak-off pressure (LOP) is reached when the relationship between pressure increase and volume of fluid pumped deviates from linear. This occurs when fluid begins to diffuse into the formation at a more rapid rate as the rock begins to dilate. Generally, a LOT is a test that finishes immediately after LOP is reached.
Features:
1) Panel with the following parameters: pump pressure, choke pressure, mud pump speed, strokes totalizer, flow rate, mud weight and volume;
2) Intuitive graphical interface: Instruments with pointers to the parameters: pump pressure, choke pressure and open/close hydraulic choke;
3. Graph Options:
– Pressures Pump / Choke and Volume Pumped versus Pumping Time;
– Pressures Pump/ Choke and Pumping Time versus Volume Pumped;
4) Panel with alarms: pump failure, bop failure and bop status;
5) Toolbar with buttons: Data File, Well Config, Restart, Ranges, Set Alarms, Graph Limits, Pause/Continue, Restart, Set BOP, Send by email, about;
6) Set drillstring with drillpipe1, drillpipe 2, heavy-weight, drillcollar1 and drillcollar2;
7) Select floating rig or land rig;
8) Select unit systems: Metric, SI, field1 (imperial) and field2 (mix);
9) set fluid parameters: mud weight, plastic viscosity, yield point and initial gel;
10) Select rheological models: Power or Bingham;
11) Set gradients: absorption and fracture;
12) Set jet nozzles or fixed TFA;
13) Set choke parameters and BOP test pressure;
14) Vertical or Slant Well Type (KOP, TVD and Measured Depth);
15) Set surface circulation equipments (mud pump and lines);
16) Save configuration to data files;
17) Select circulation options: drillpipe -> riser and drillpipe -> choke, Close/Open (Hard shut-in) the well;
18) Reset alarms: pump failure: max pump speed, max pump pressure and max pump power;
19) Register the pressures at the kill speed ;
20) Show schematic of well with drillstring and riser, casing, liner and open hole;
21) Shut-in the well using hard method;
22) Circulation on slow rate (kill speed);
23) Useful for filling of Standardized Kill Sheets for Well Control;
24) Useful for Filling of Previous Recorded Sheets;
25) Analize of the Choke Line effect in Maximum Choke Pressure;
26) Analize of the Effect of porosity and permeability on absorption curve;
27) Simulation of the Leak-Off Test operation and Graphical Analize of the Leak-Off Test
28) Capacities and Volumes calculations;
29) Hydrostatic and critical pressures calculations;
30) Hydraulics calculations;
Basic Exercise:
1. Close BOP and Choke;
2. Set Mud Pump Speed;
3. Monitor the Choke Pressure;
4. When the pressure deviates from linear, stop the mud pump;
5. Wait until the choke pressure stabilize;
6. Tap on graph to obtain data;
7. Open choke to bleed until choke pressure to zero;
Notes:
1. Set fracture gradient > absorption gradient;
2. The Absorption curve is function of porosity and permeability.
3. Tap with finger and moving it in the graph area to obtain Choke Pressure,
Equivalent Density, Equivalent Gradient, Volume Pumped and Pumping Time.

contact@wellcontrol.com.br
Well Control Methods for iPhone and iPod Touch 2.6 now available on the App Store
Well Control Methods 2.6 for iPhone and iPod Touch
New in this update:
– Support for iOS 6 and iPhone 5;
– Ability to select units also per parameter;
– Ability to import data from other apps;
– Recalculate DP as necessary to surface automatically with bit on bottom when editing BHA or Well Depth;
– Improved printing and email attachments with retina display
– Changed hydrostatic factor from 0.052 to 0.051948 (due the new method to choice units)
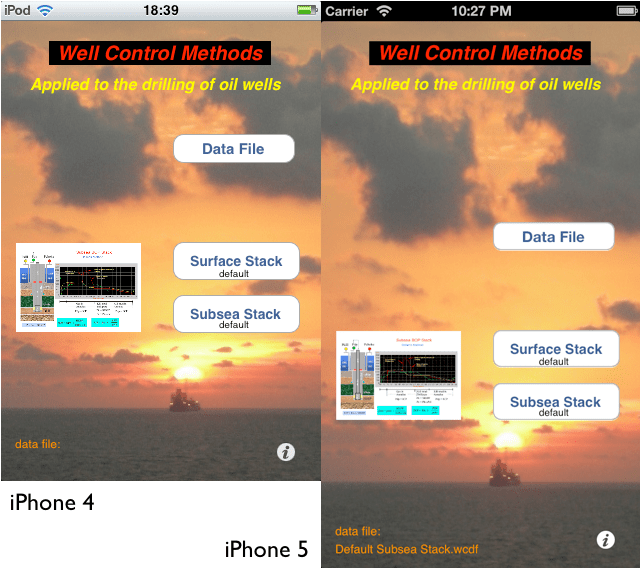
This application uses the basic calculations of the methods to control oil wells after the occurrence of kick during drilling operations on floating platforms and land rigs.
This app is completely interactive and allows users to define a wide variety of parameters for oil wells and unit system, save data and more.
It is can be applied in the oilfield and also help on understanding the methods of the well control.
For Simulation, use the another app “Well Control Simulation”.
For new features, report bugs, improvements and suggestions please contact us: contact@wellcontrol.com.br
Well Control Methods:
1. Driller’s Method
2. Wait and Weight
3. Dynamic Volumetric
4. Static Volumetric – Migration / Bleed
5. Static Volumetric – Lubricate / Bleed
Others:
6) Calculations of Riser Safety Margin;
7) Included the formulas;
8) Ability to work with multiple files;
9) Sections: Riser, Casing, Liner and Open Hole;
10) Pop-up view to alert user about invalid values;
11) Send resume of methods by email.
12) Show graph theoretical of the methods.
13) Set drillstring with drillpipe1, drillpipe2, heavy weight, drillcollar1 and drillcollar2;
14) Select floating rig or land rig;
15) Select unit systems: Metric, SI, field1 (imperial) and field2 (mix);
16) set fluid parameters: mud weight, plastic viscosity, yield point and initial gel;
17) Select rheological models: Power or Bingham;
18) Set gradients: formations and temperature;
19) Set jet nozzles or fixed TFA;
20) Vertical or Slant Well Type (KOP, TVD and Measured Depth);
21) Set surface circulation equipments (mud pump and lines);
22) Save configuration to data files;
23) Show schematic of well with drillstring;
23) Useful for filling of Standardized Kill Sheets for Well Control;
24) Useful for Filling of Previous Recorded Sheets;
25) Capacities and Volumes calculations;
26) Hydrostatic and critical pressures calculations;
27) Hydraulics calculations;
 |
 |
 |
 |
contact@wellcontrol.com.br







You must be logged in to post a comment.