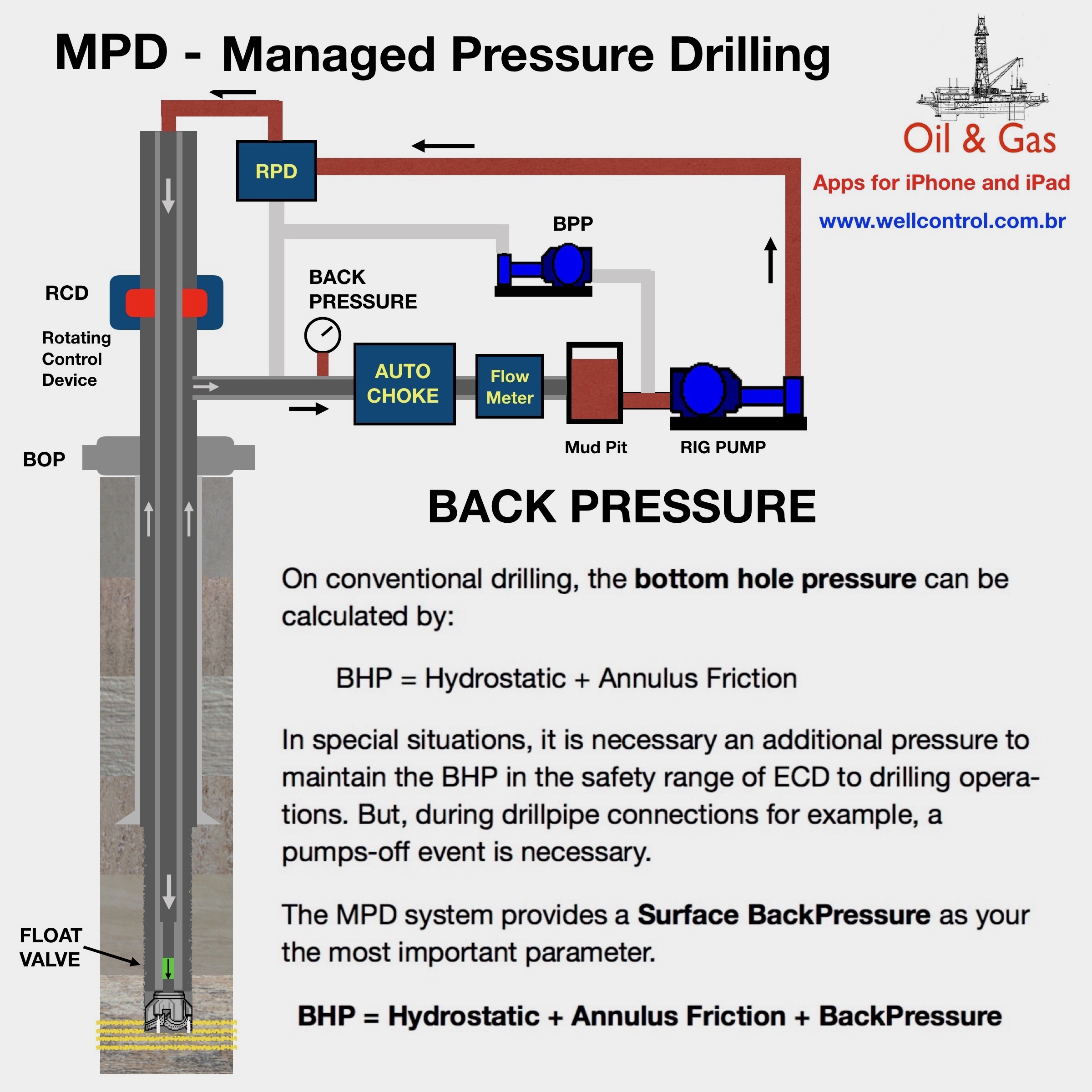
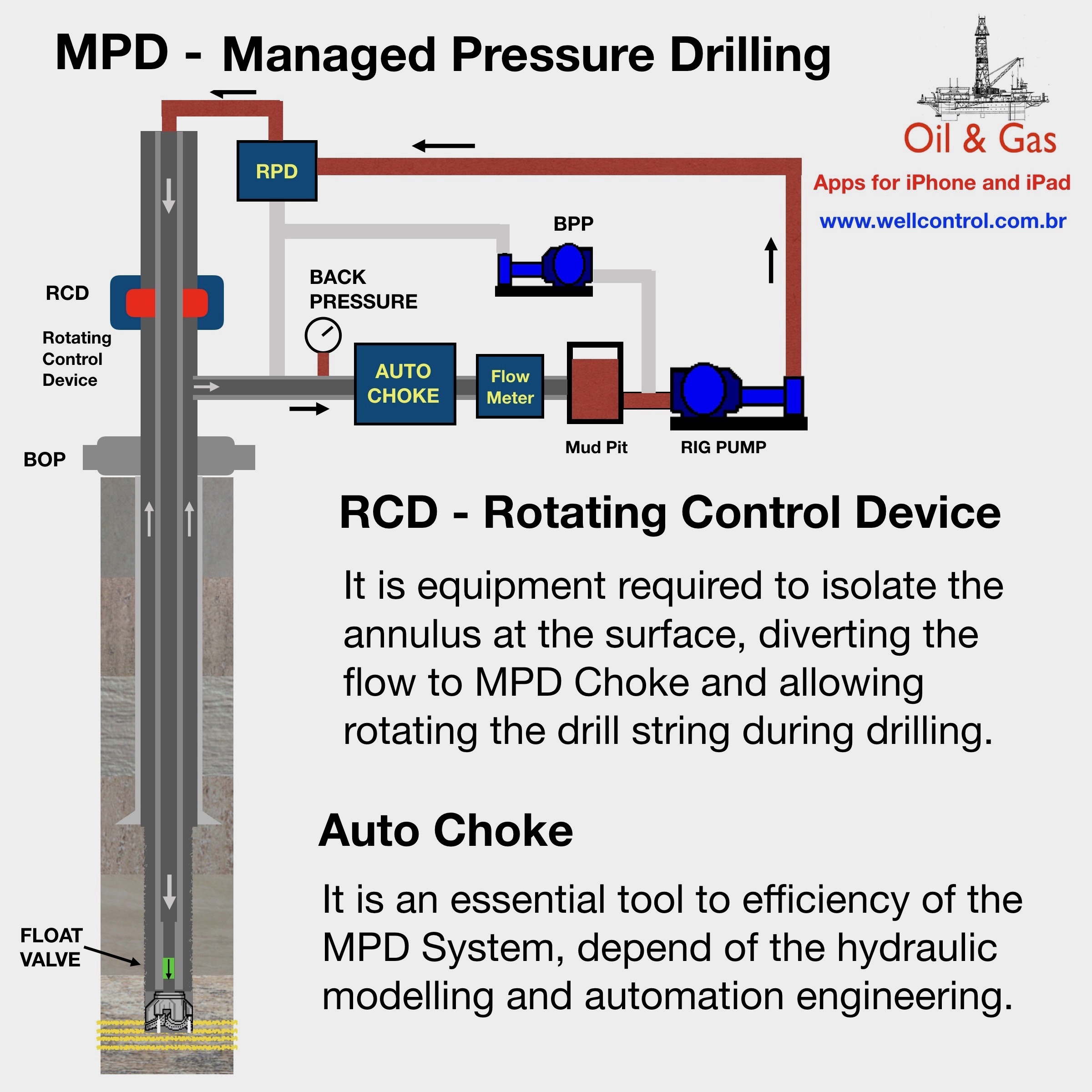
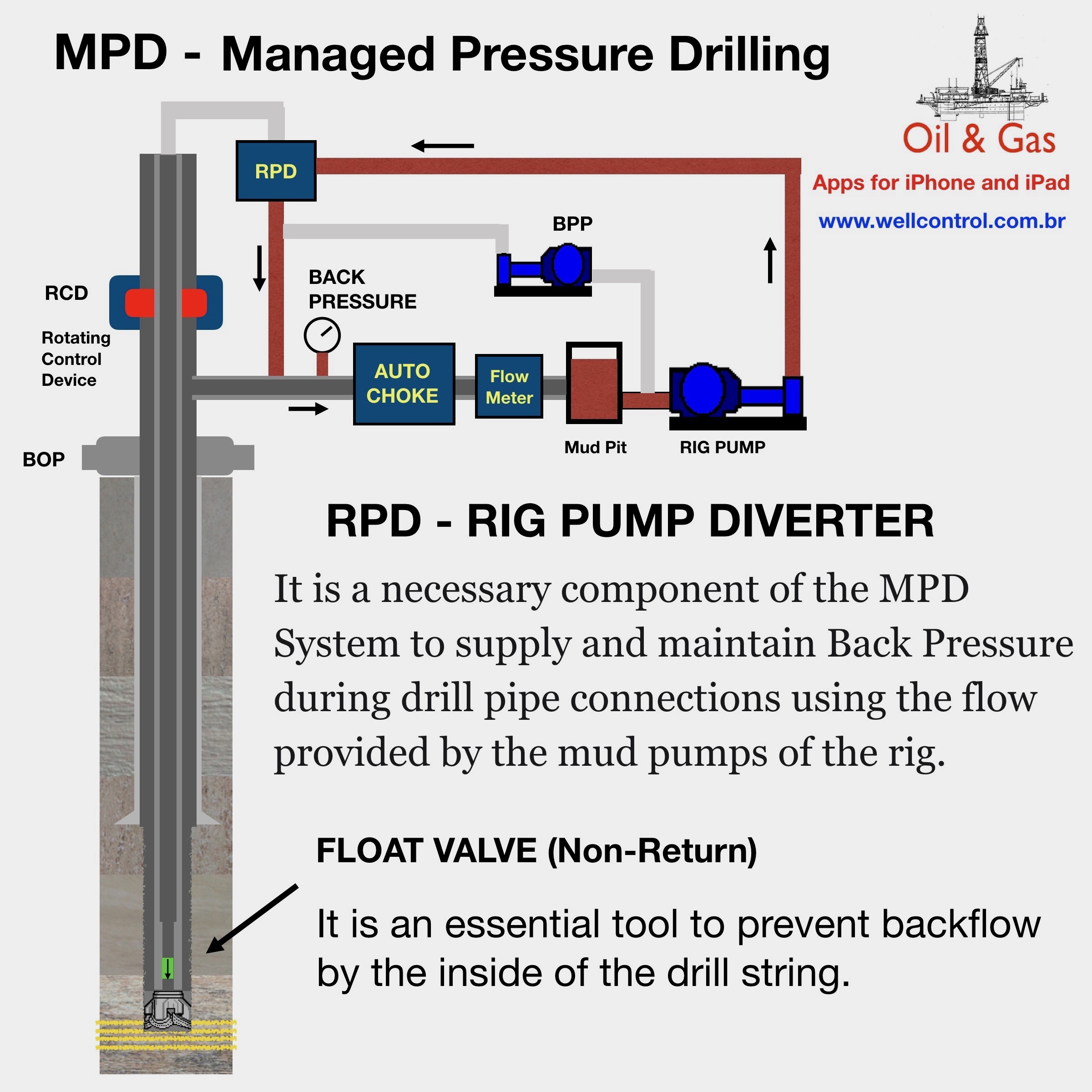
Kick Tolerance as Maximum Kick Volume
Kick Tolerance as Maximum Kick Volume
Concepts
There are several concepts about kick tolerance, but this article only deals with the concept of kick tolerance as the maximum kick volume.
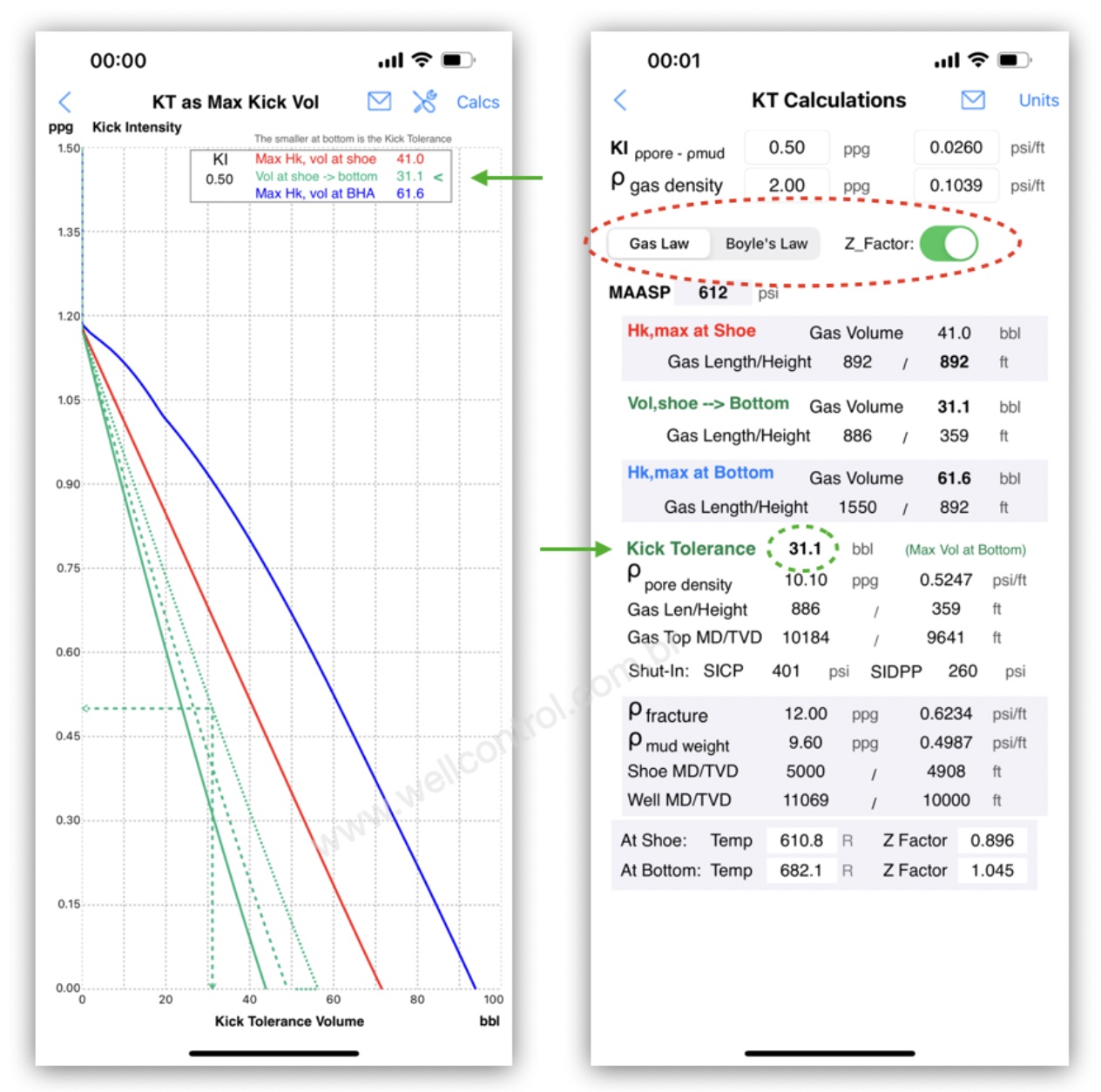
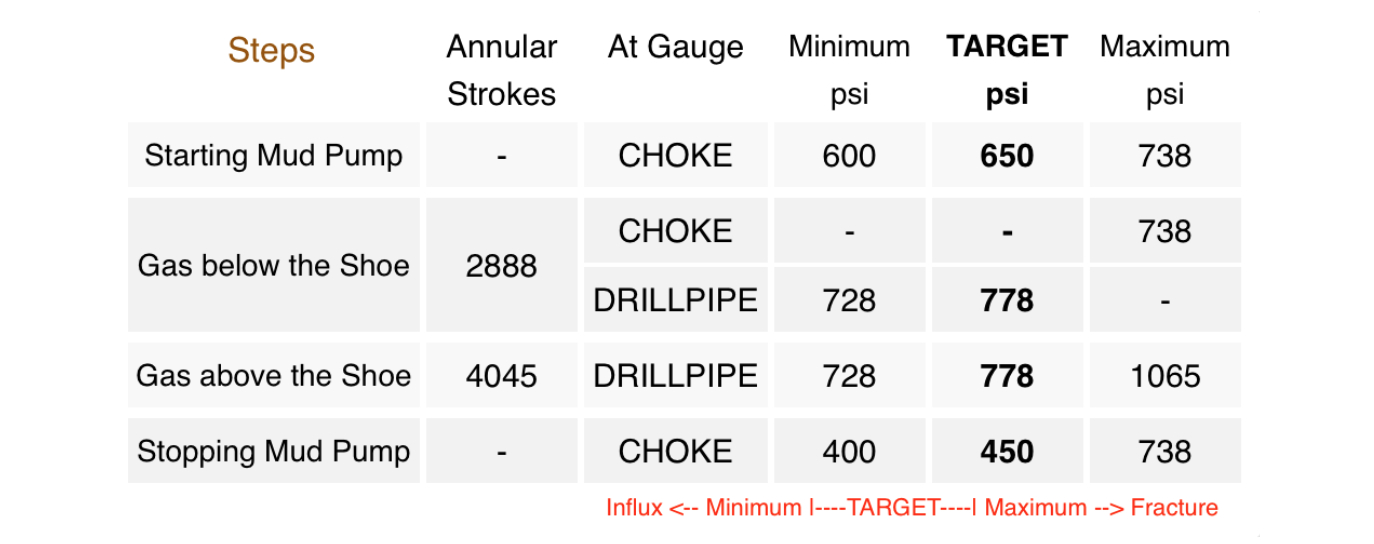
Kick Tolerance is the maximum kick volume that can be taken into the wellbore and circulated out without fracturing the formation at weak point (normally at shoe depth), given a diference between pore density (equivalent) and the mud weight in use.
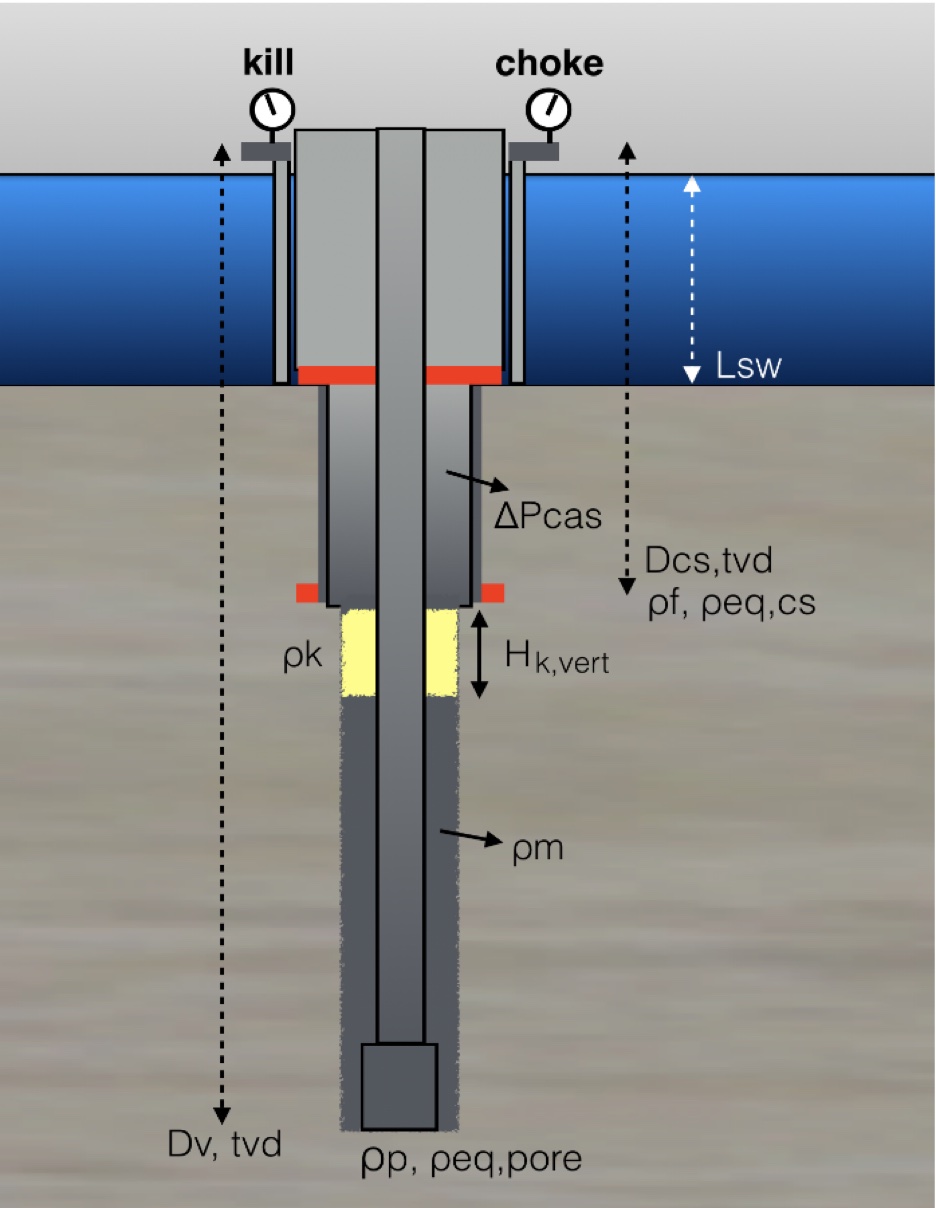
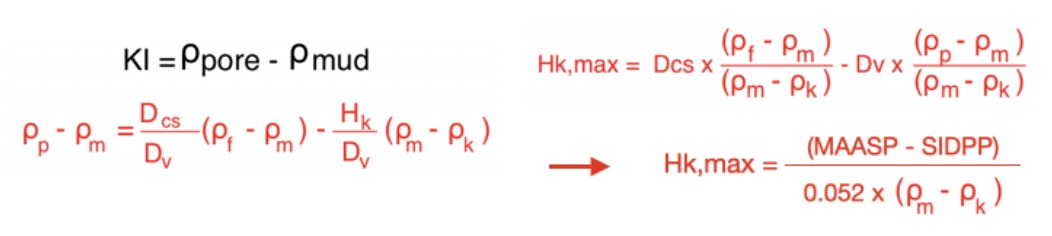
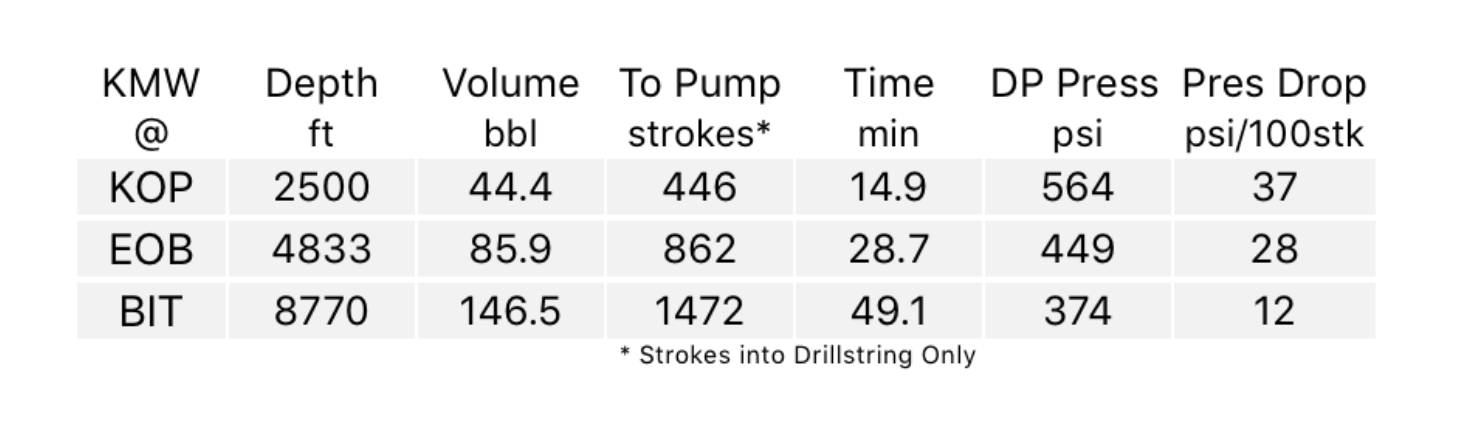
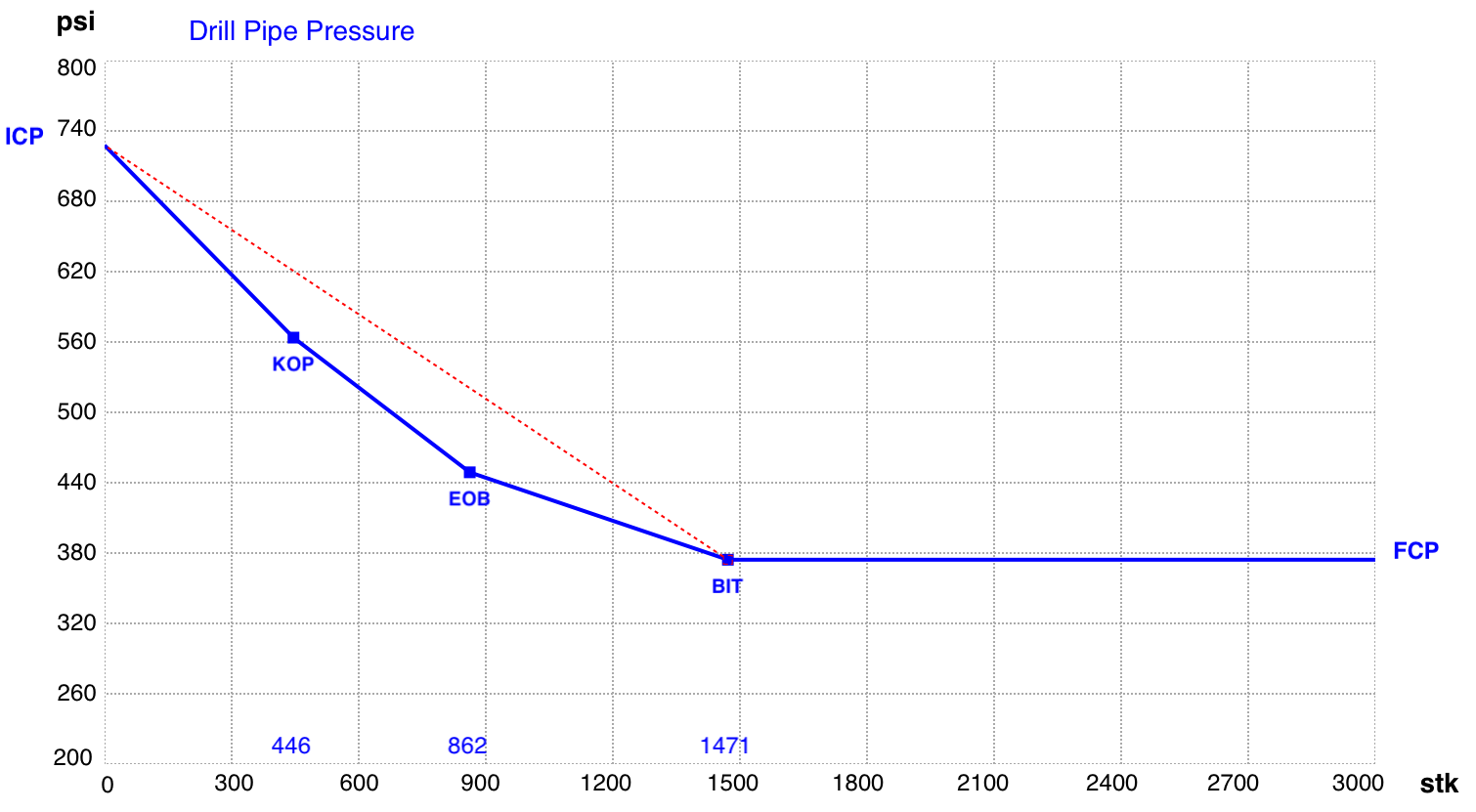
The maximum gas bubble height in the open hole can occur either at the bottom around the BHA (Bottom Hole Assembly) or when the volume is at its maximum when the gas reaches the the casing shoe.
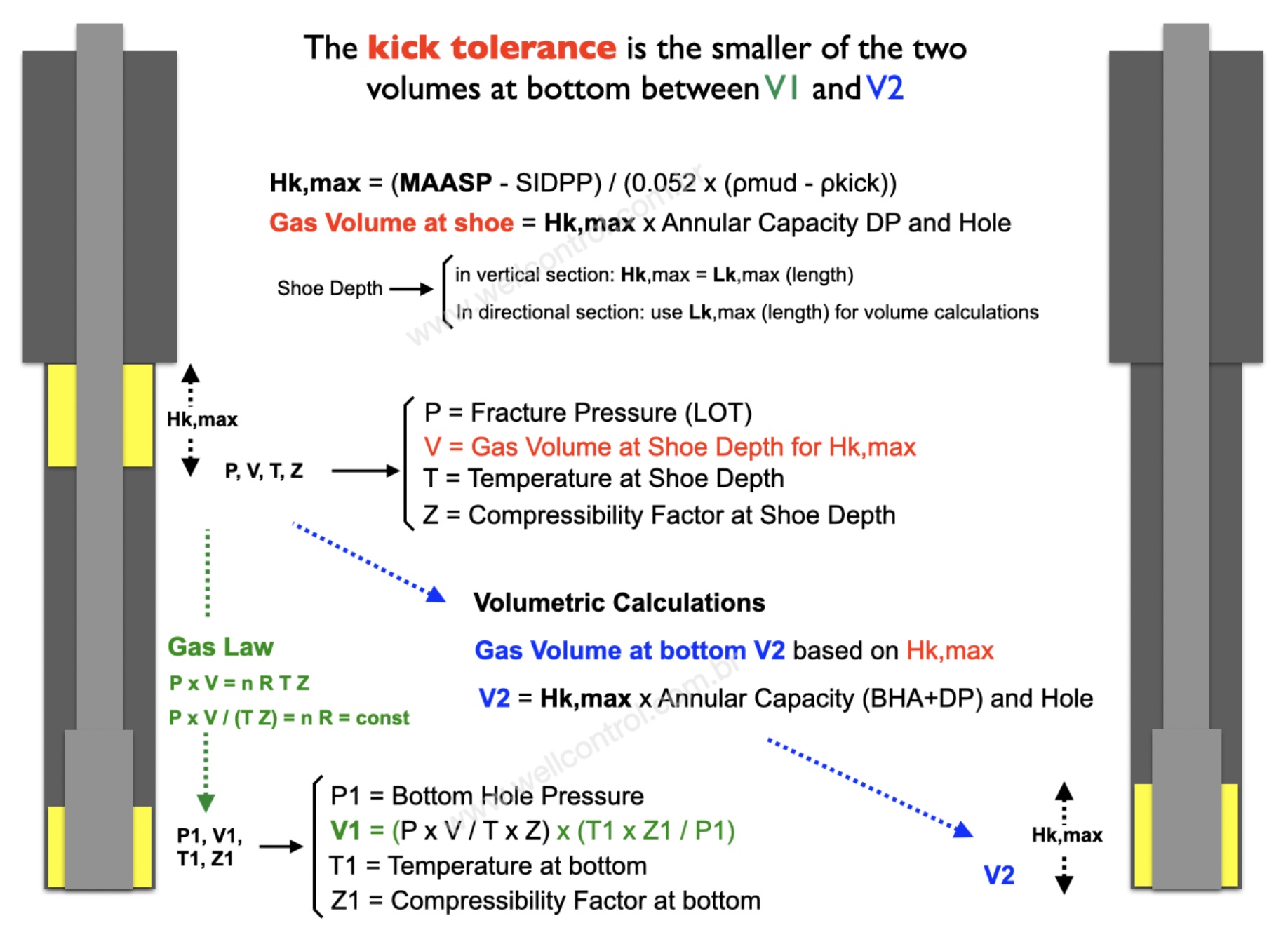
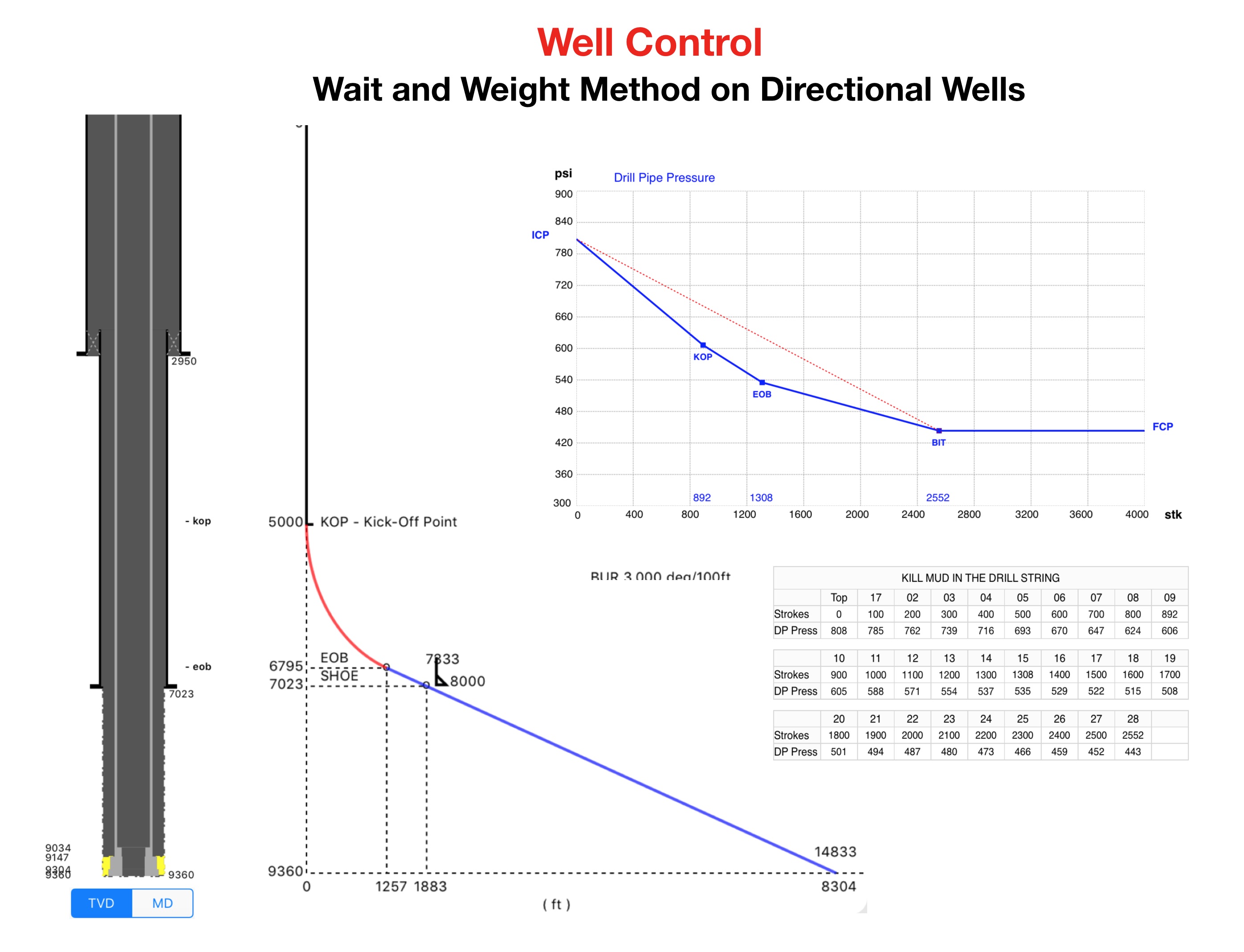
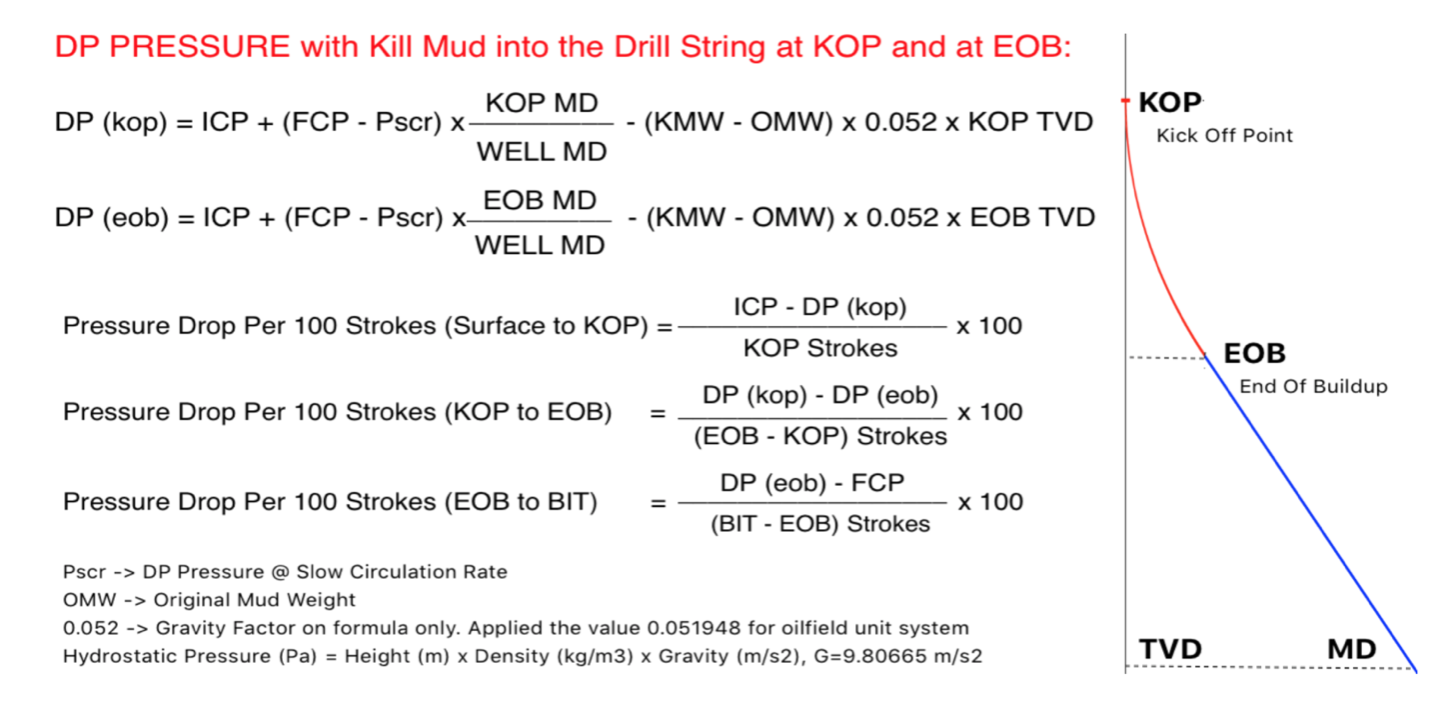
Calculating the Gas Volume at shoe depth based on the Maximum Influx Height
Maximum Gas Volume at shoe = Hk,max x Annular Capacity DP and ID Hole)
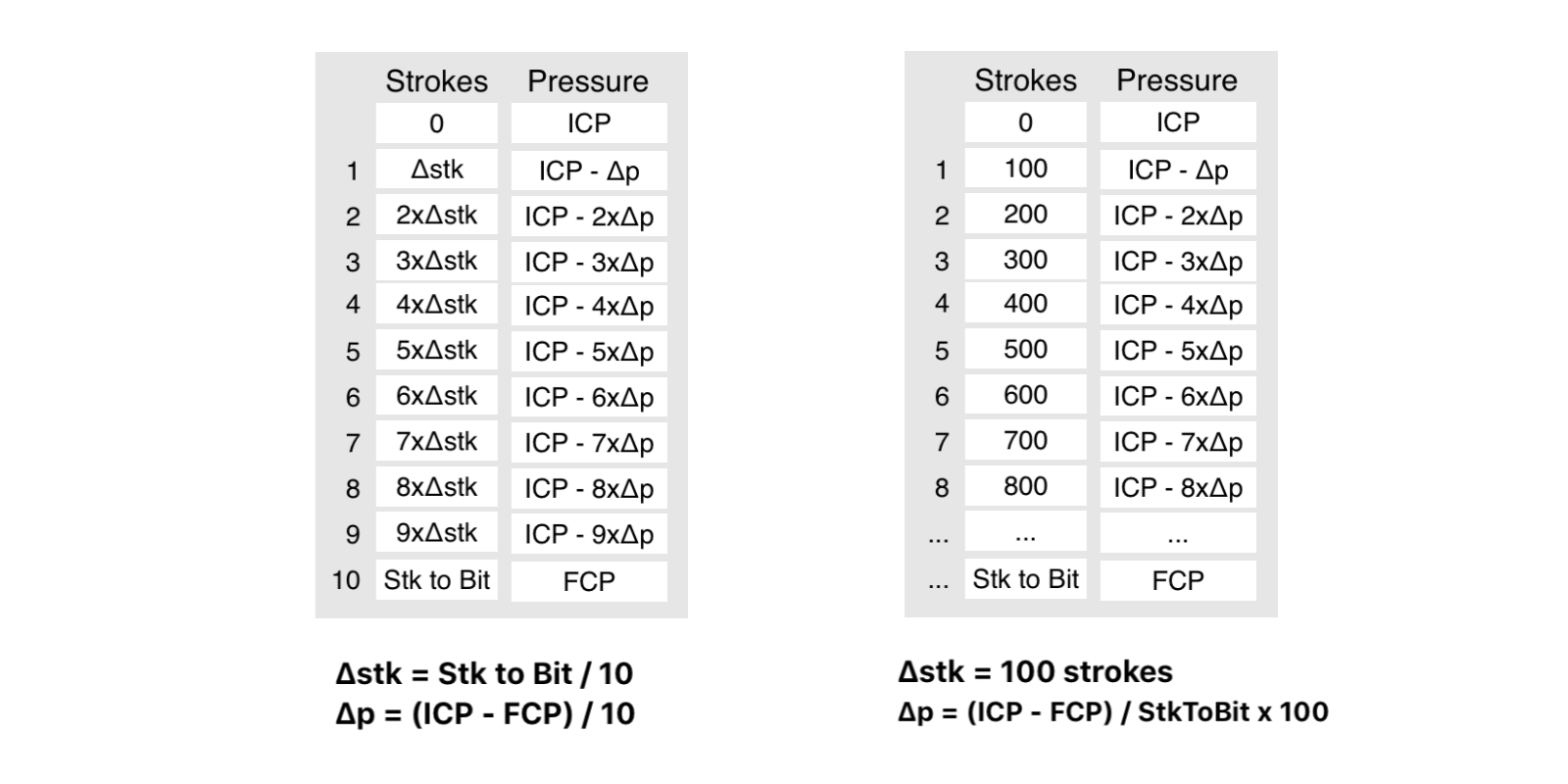
1. Calculate V1 at bottom applying the Boyle’s Law: P1 x V1 = P2 x V2 (isothermal)
V1 = Vshoe x P,fracture / P,pore
2. Calculate V2 at bottom around the BHA with height equal to Hk,max,
V2 = Hk,max x Cap,ann,bha
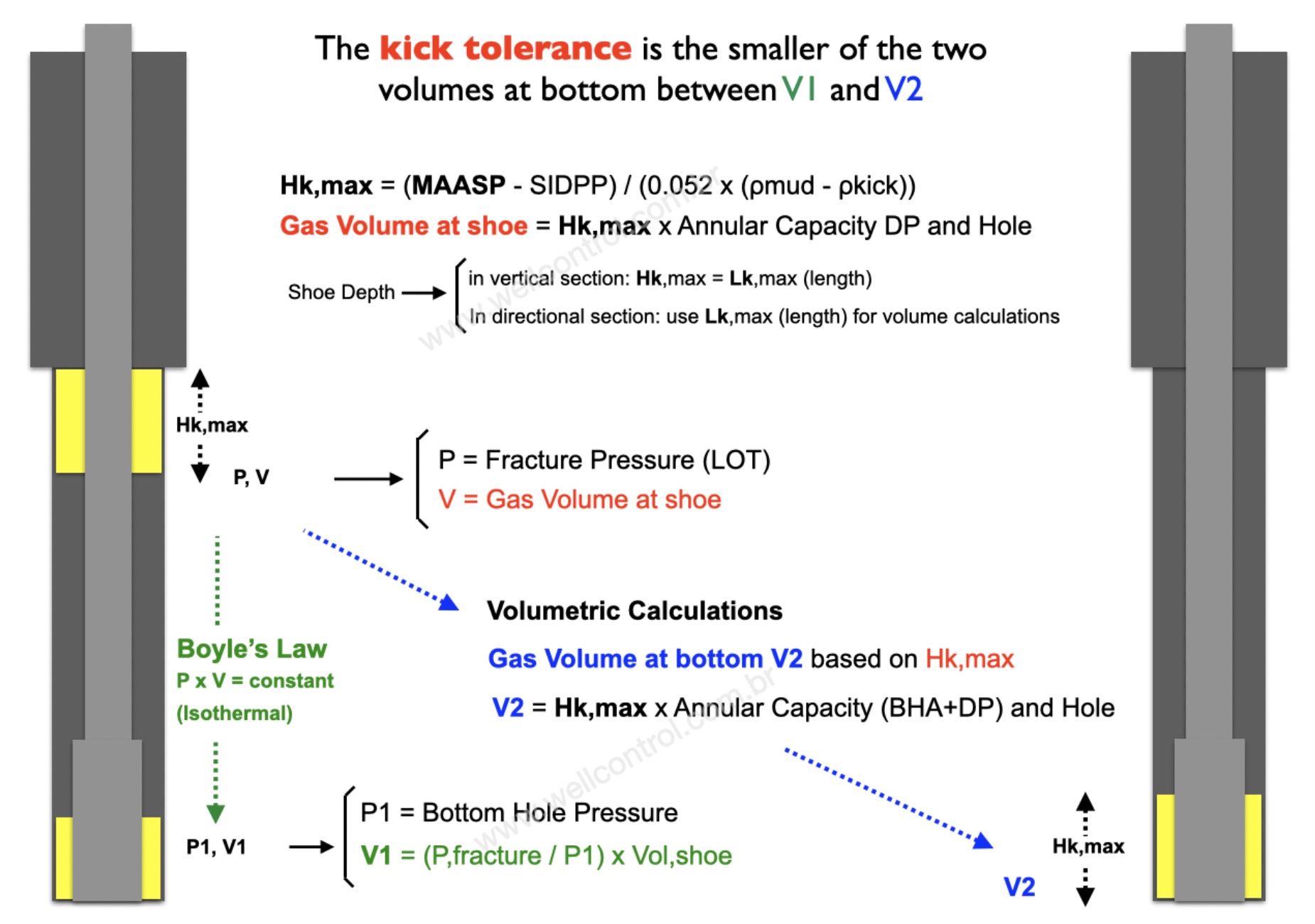
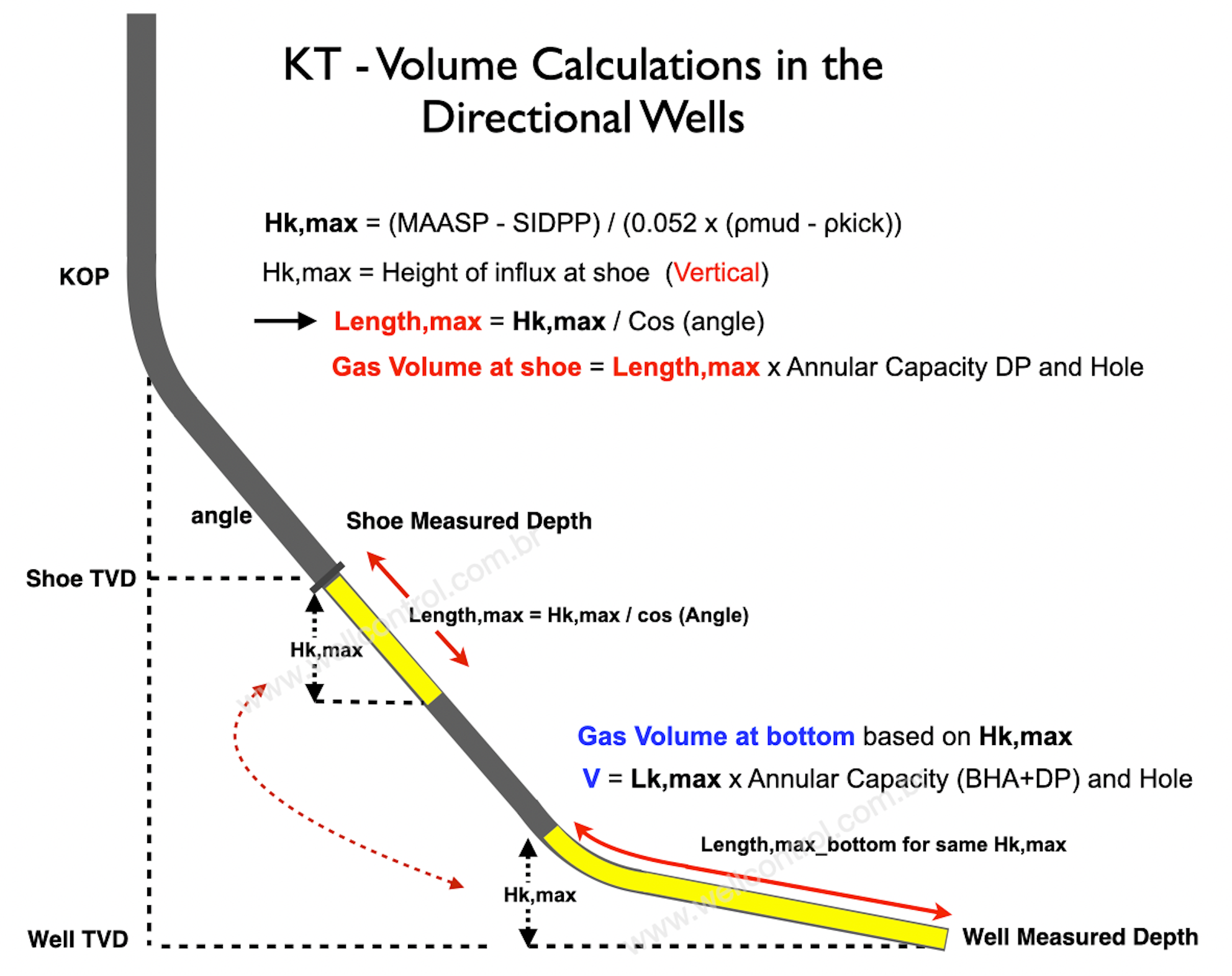
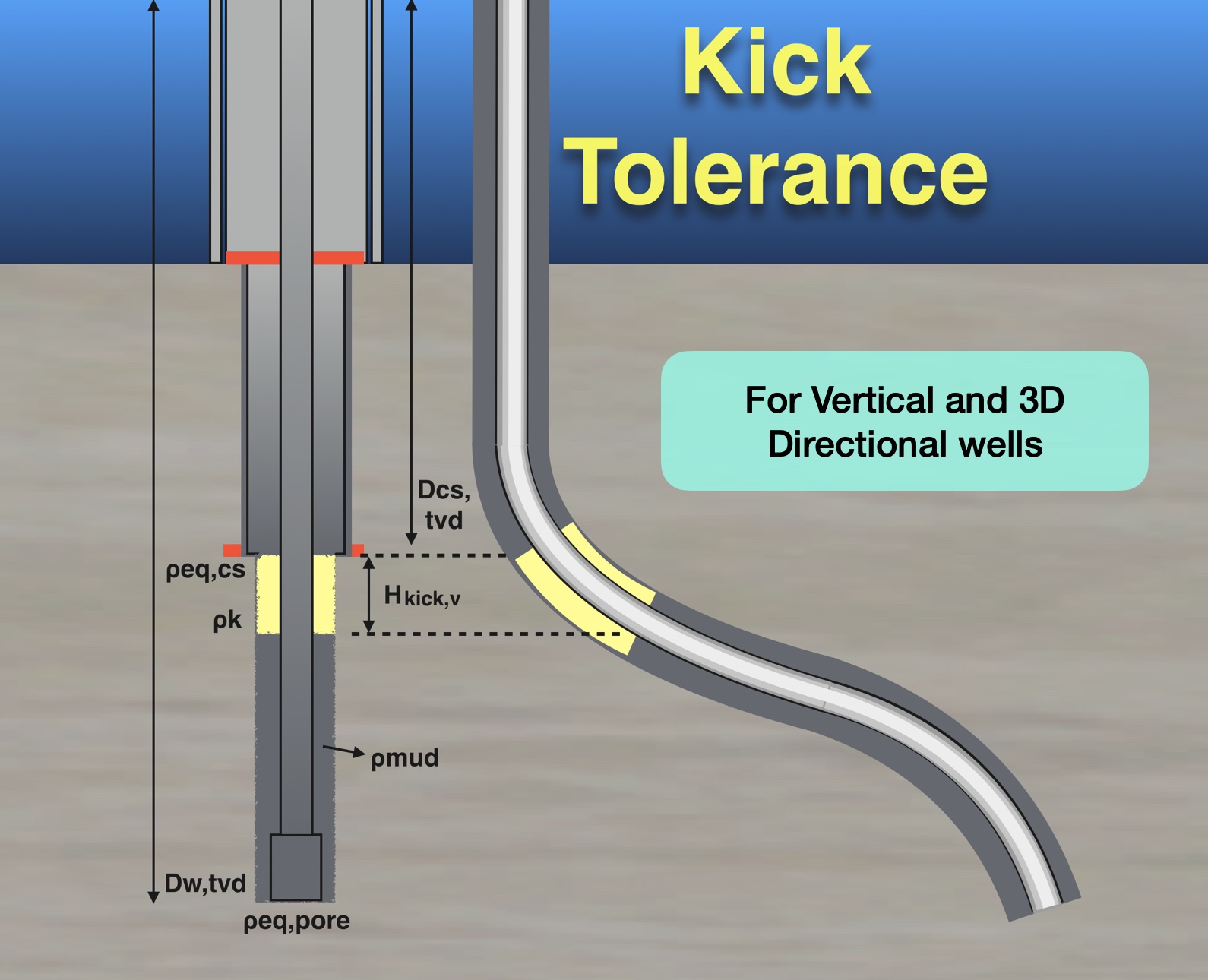
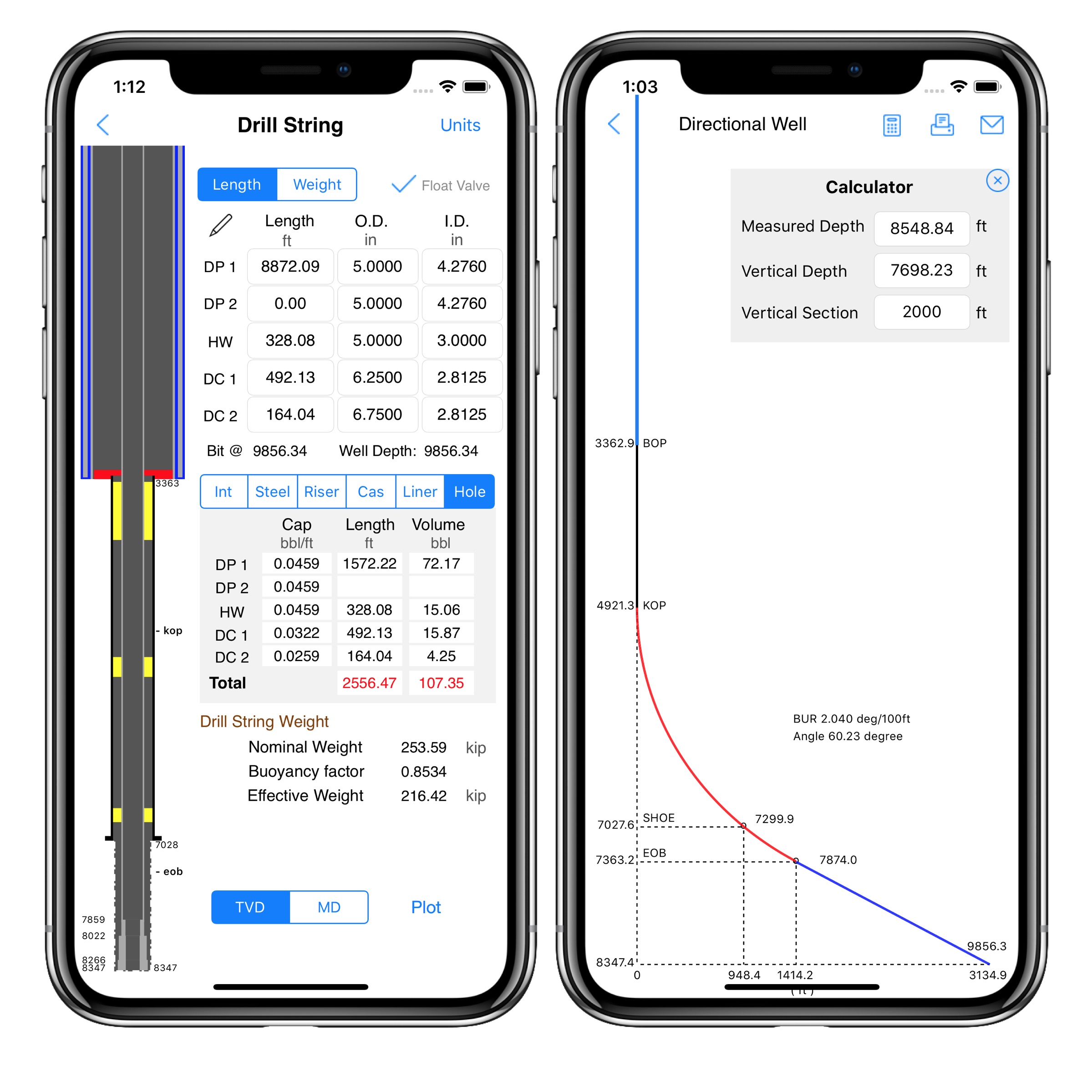
Calculating volumes for Hk,max in the Directional Wells
Boyle’s Law
Normally, the formula used only considers Boyle’s Law, without considering that there is a temperature variation from the bottom of the well to the depth of the casing shoe.
Gas Law and Gas Compressibility Factor
For natural gas, the gas law is best applied because there is temperature variation in the well and the gas has a compressibility factor different from 1.
P x V = n x R x T x Z
P, Pressure
V, Volume
n, Number of moles
R, Constant
T, Temperature
Z, Compressibility Factor of the gas
In this case, the calculations considering the Gas Law:
V1 = (Vshoe x P,shoe) / (Tshoe x Z,shoe) x (Tpore x Z,pore / P,pore)
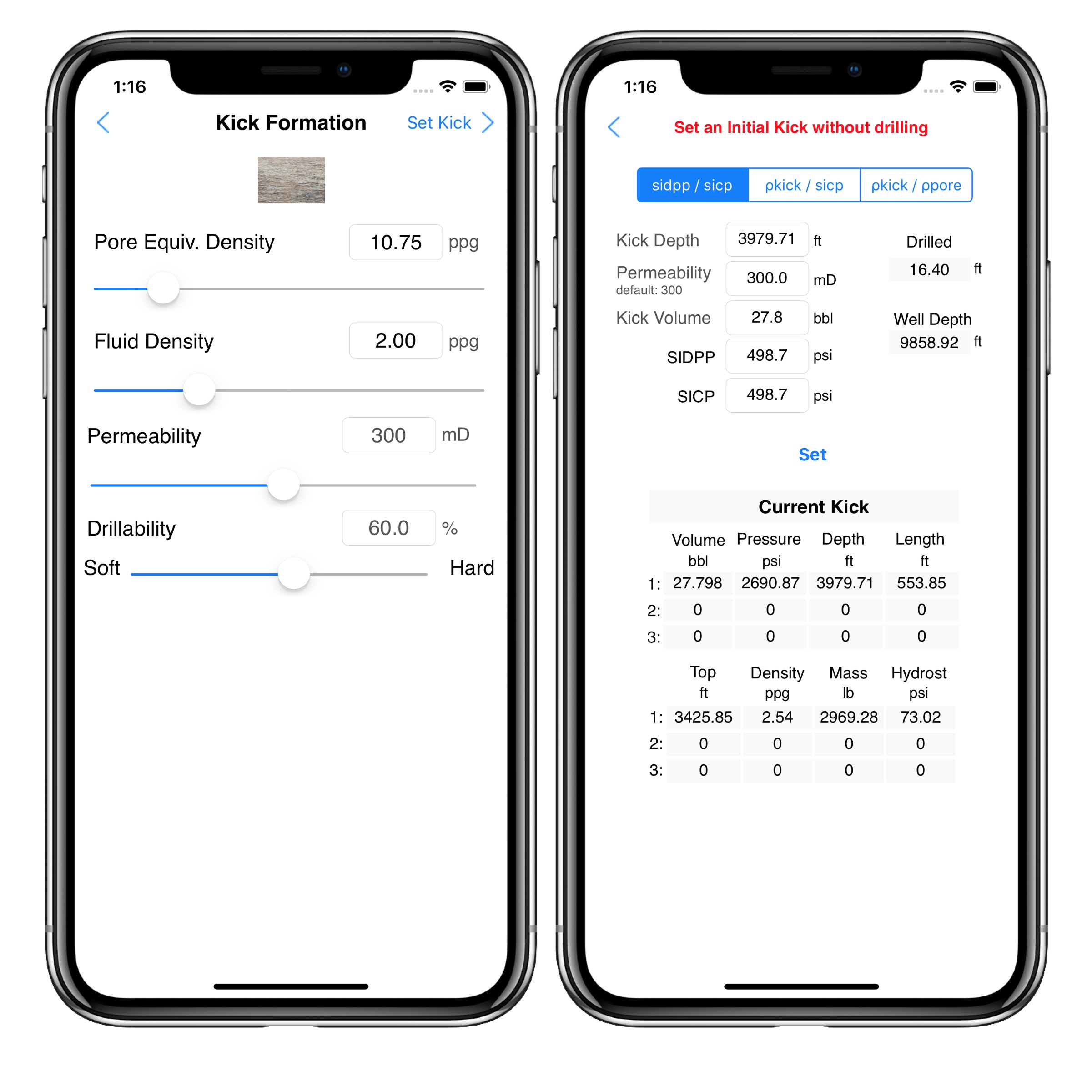
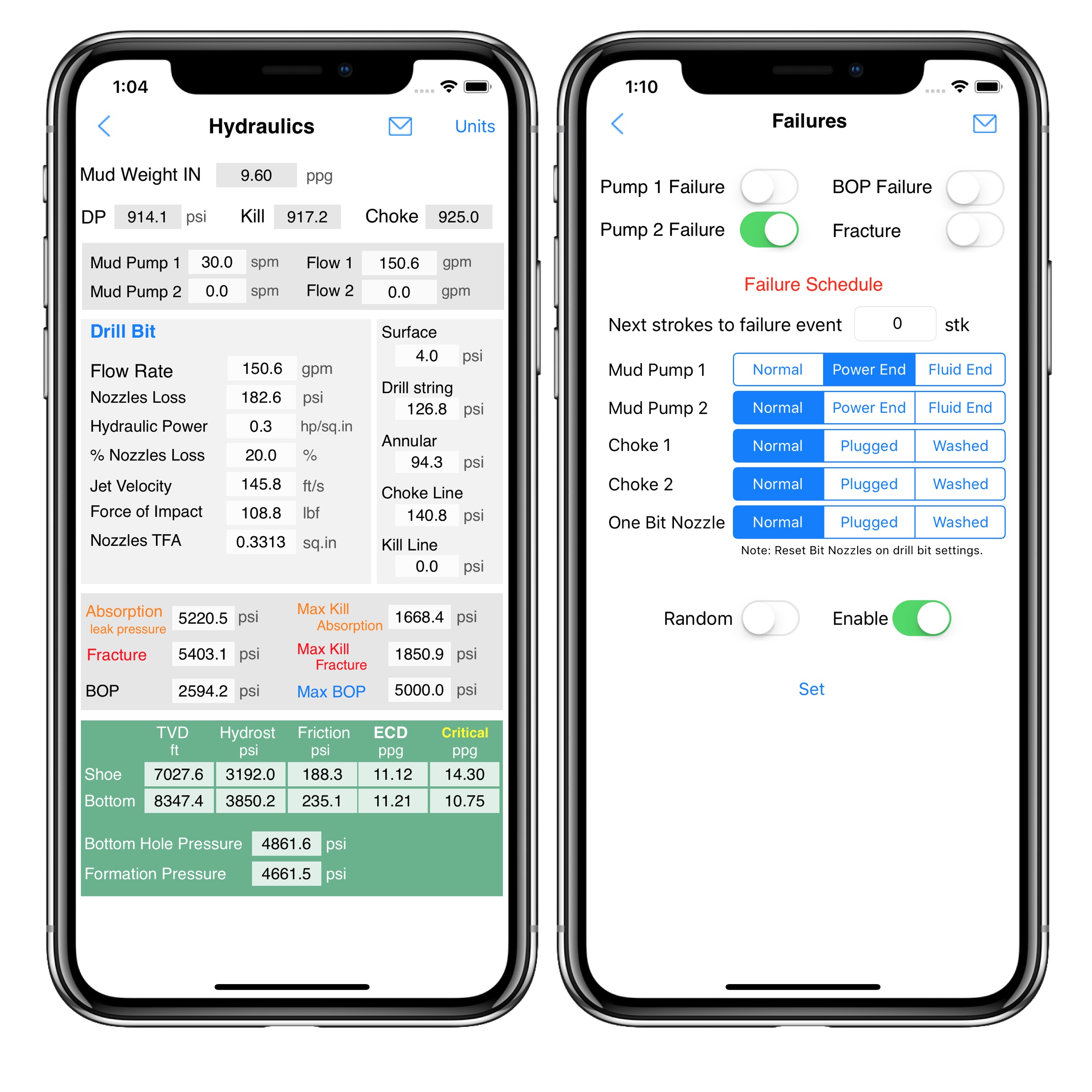
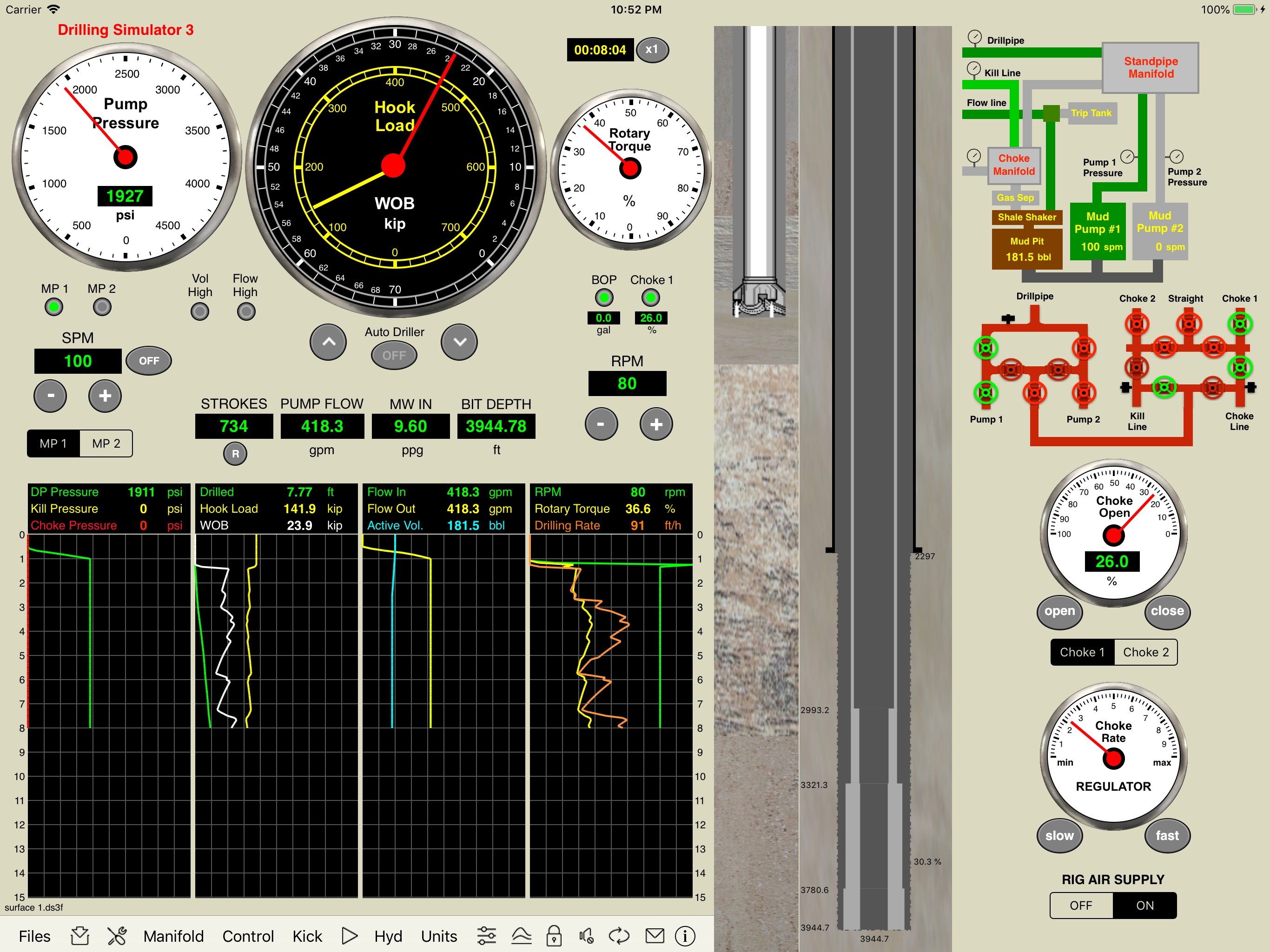
Kick Tolerance (Max Vol) application
We develop an application with options to select temperature and/or the Z-Factor of the gas. It works with vertical wells and 3D directional wells.
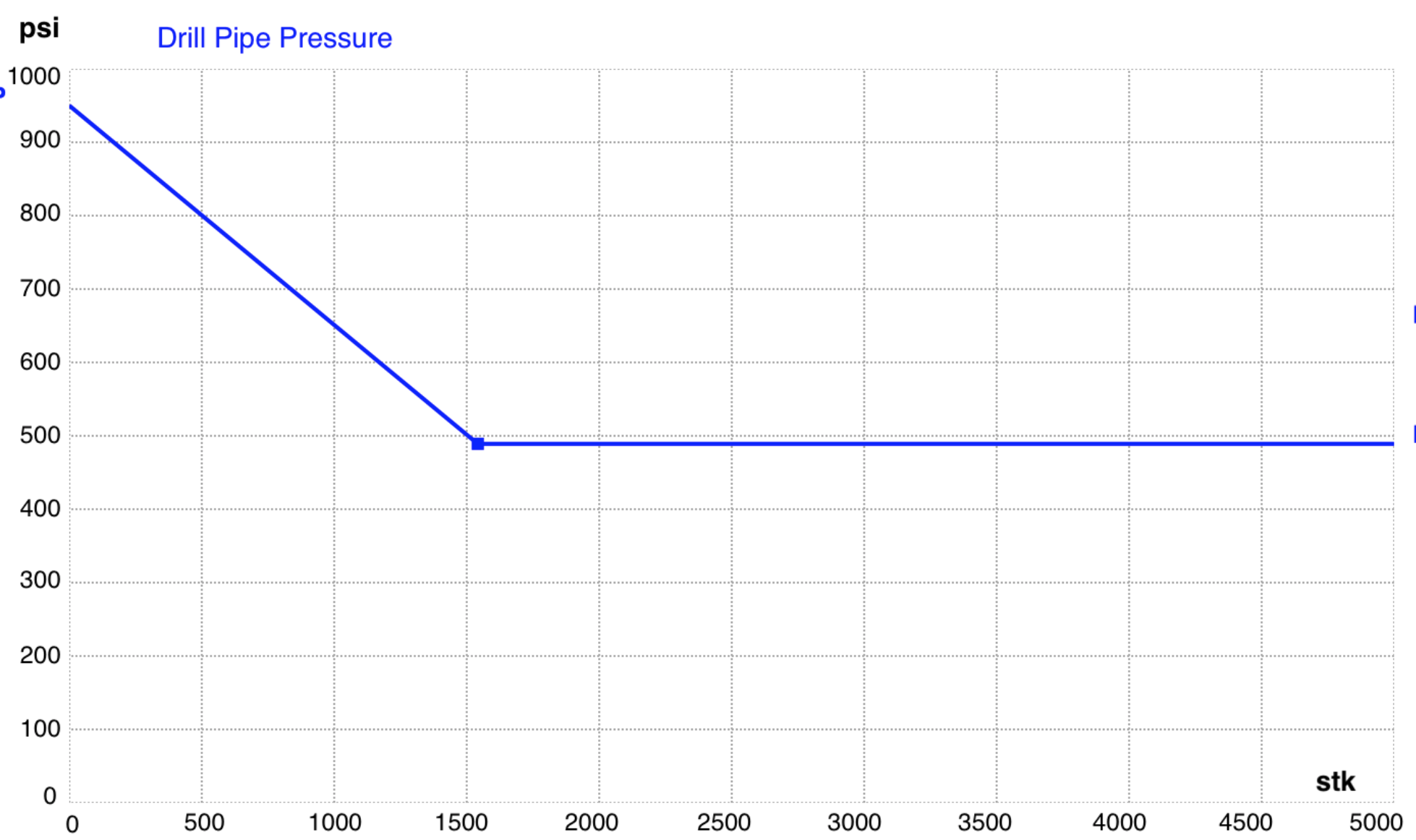
Comparing Boyle’s Law versus Gas Law
On vertical well, the result is not affected when the volume calculated at the bottom of the hole is smaller.
Using the Boyle’s Law:
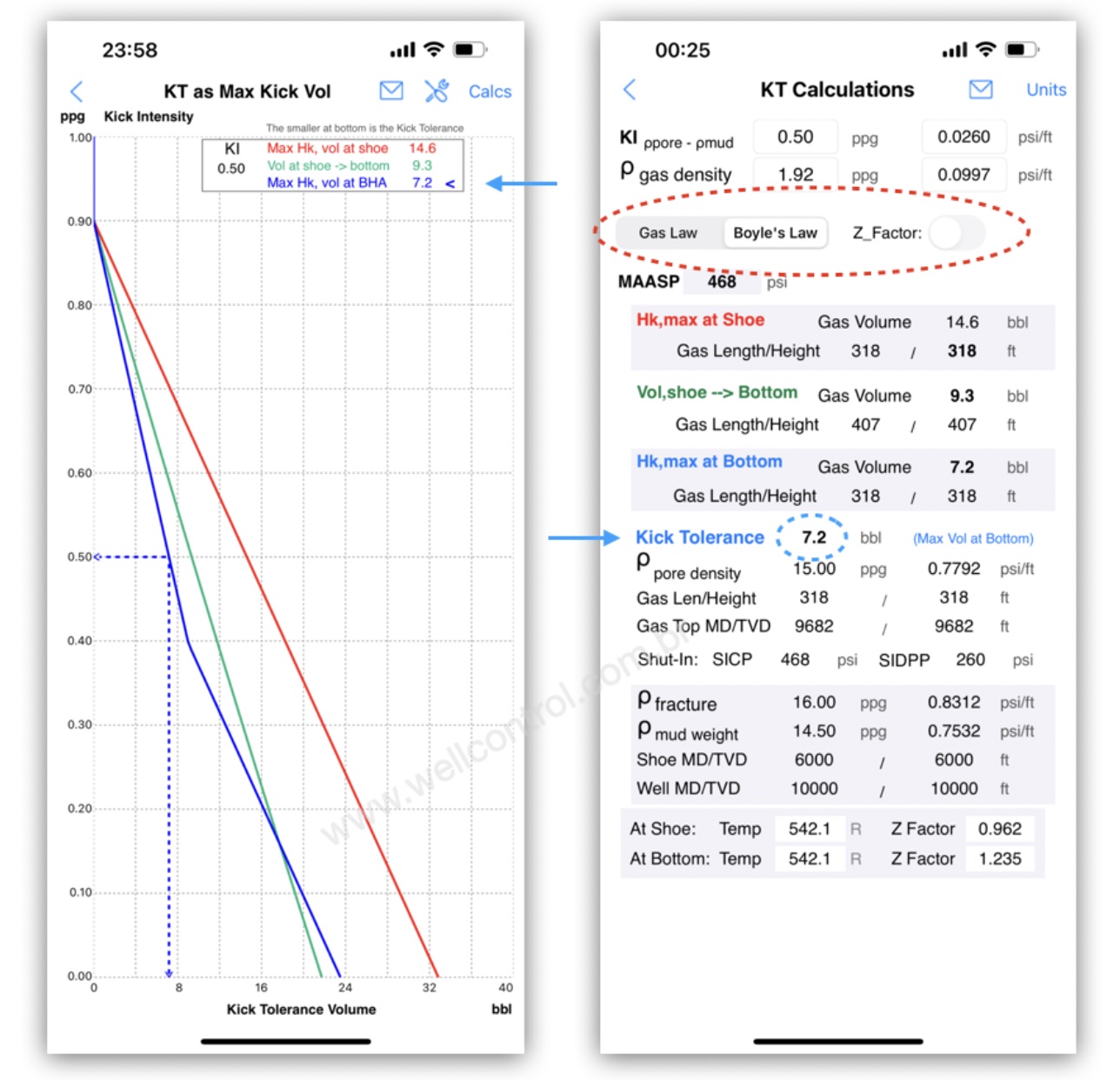
Using the Gas Law:

On directional well, the kick volume at the shoe depth converted to bottom of the hole is normally smaller and the result is affected when applying the Boyle’s Law or the Gas Law.

Note: In this directional well, the shoe depth is in a vertical section. So, height and length of gas bubble can be equal in a directional well.
Using the Boyle’s Law:
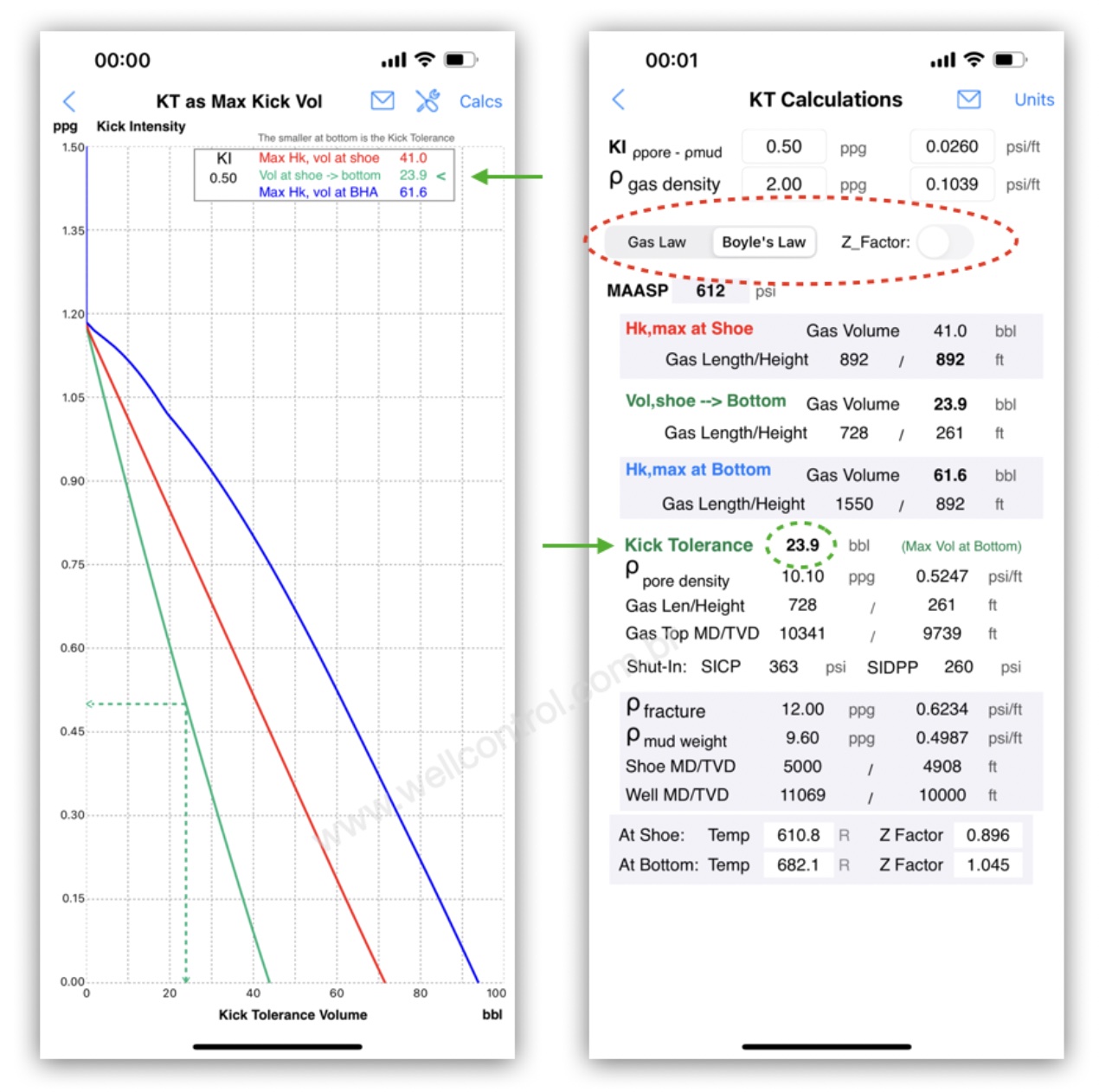
Using the Gas Law:

These apps are available in our portfolio.
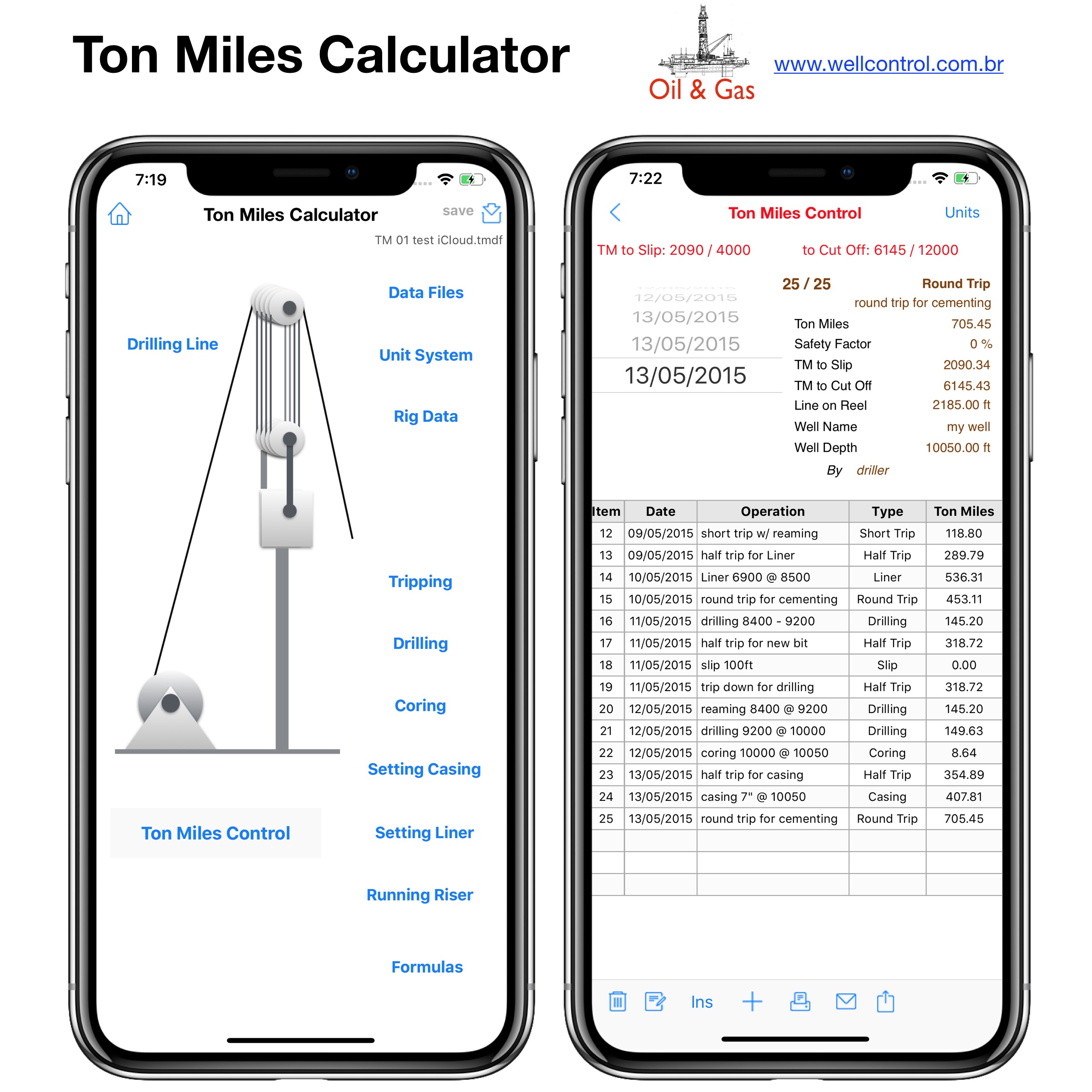
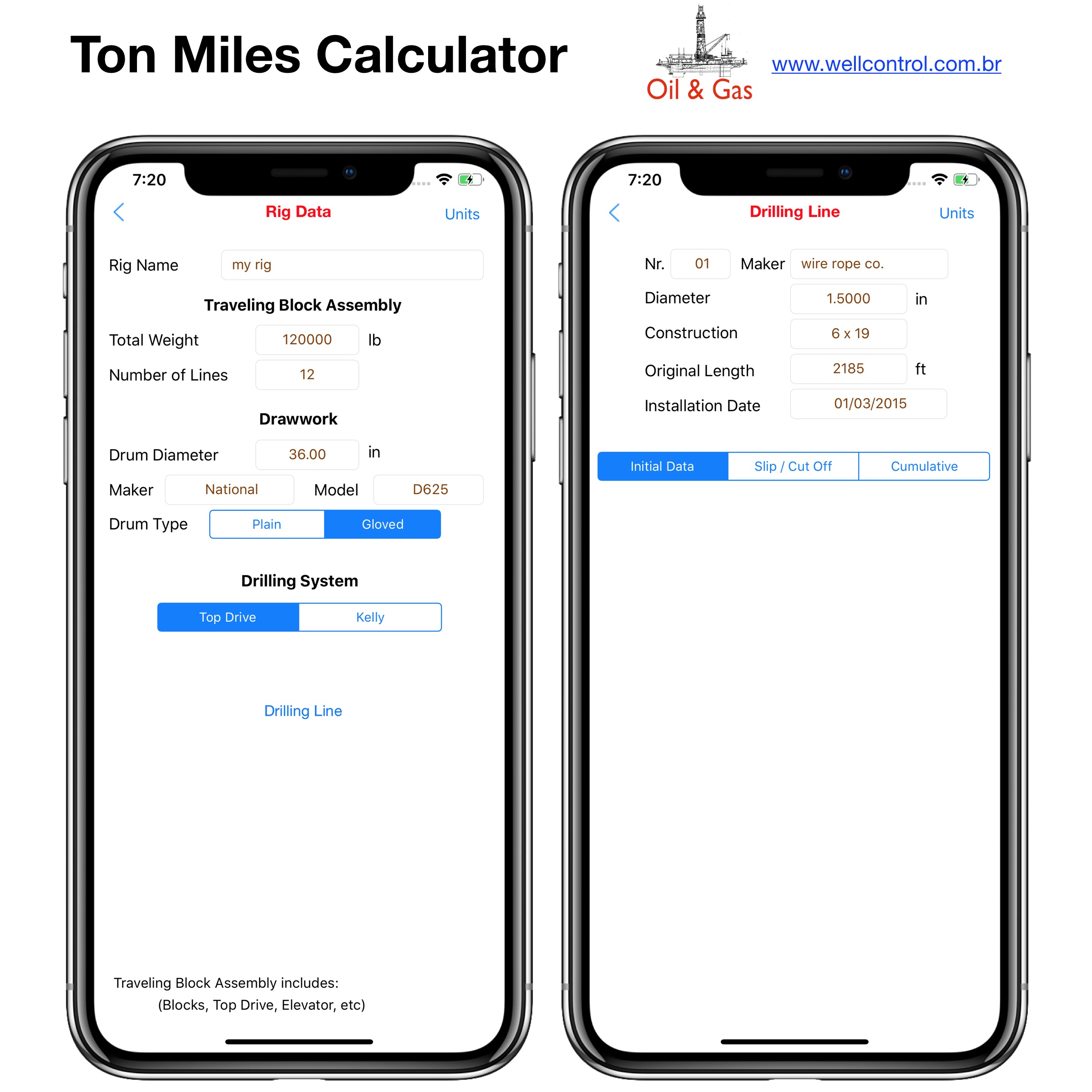
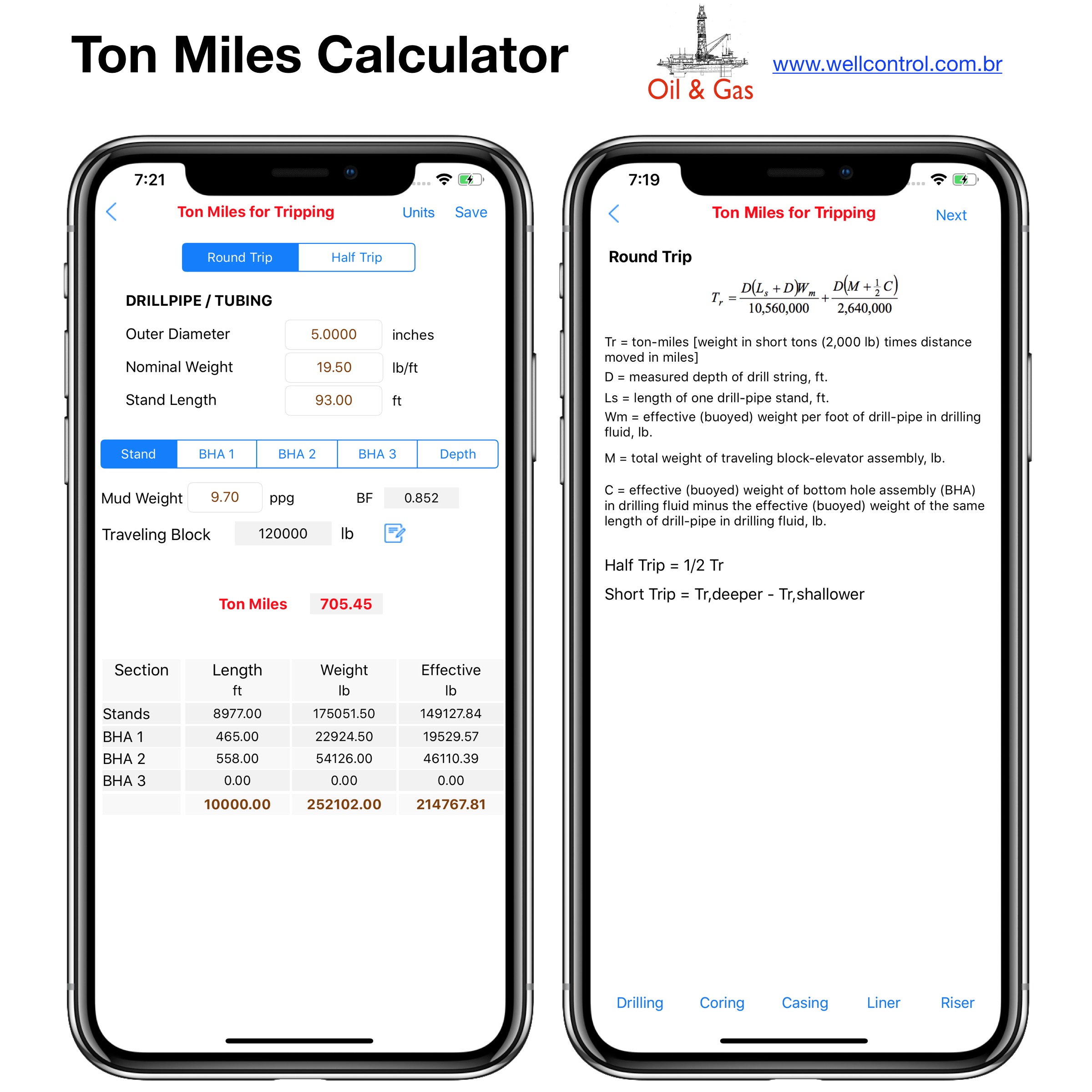
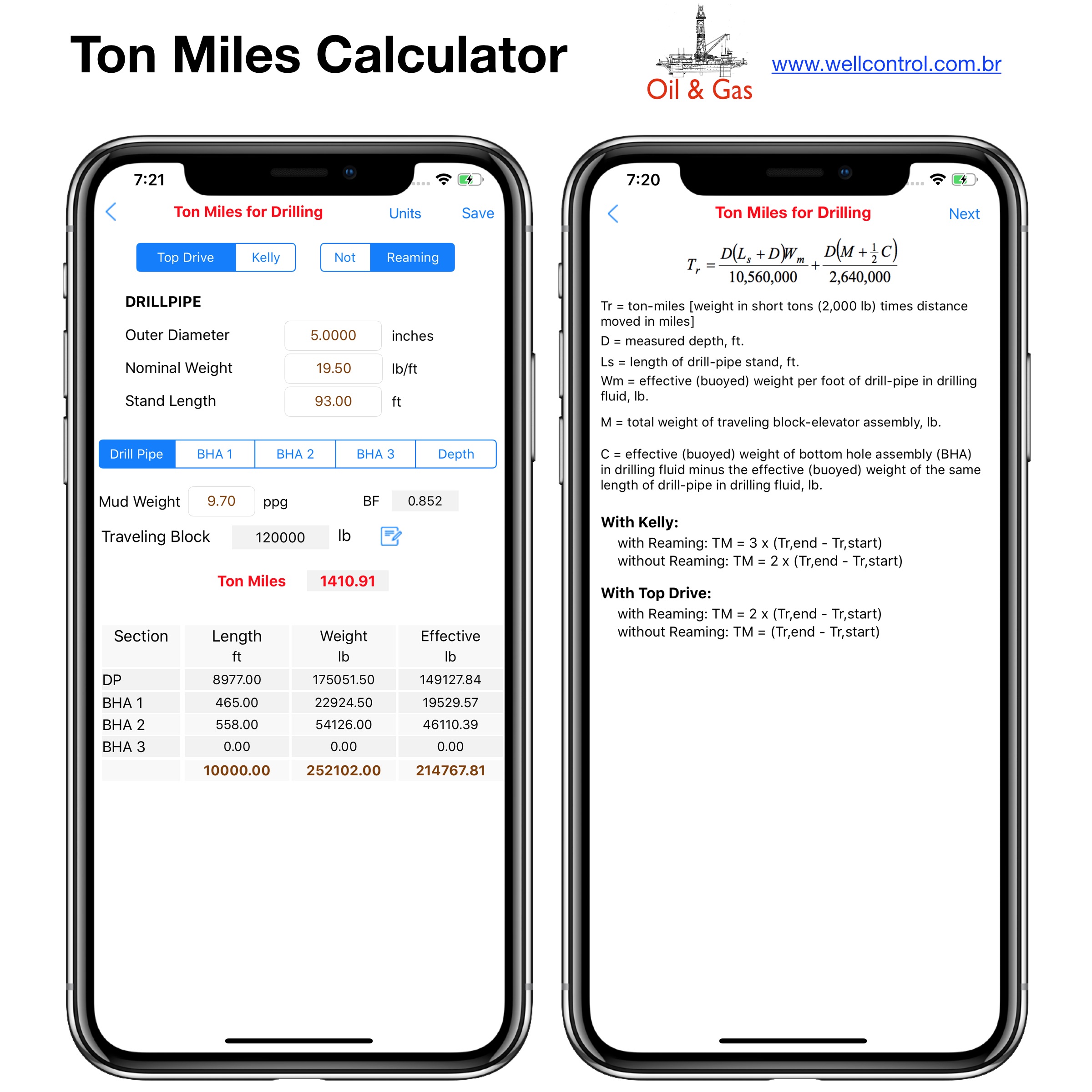
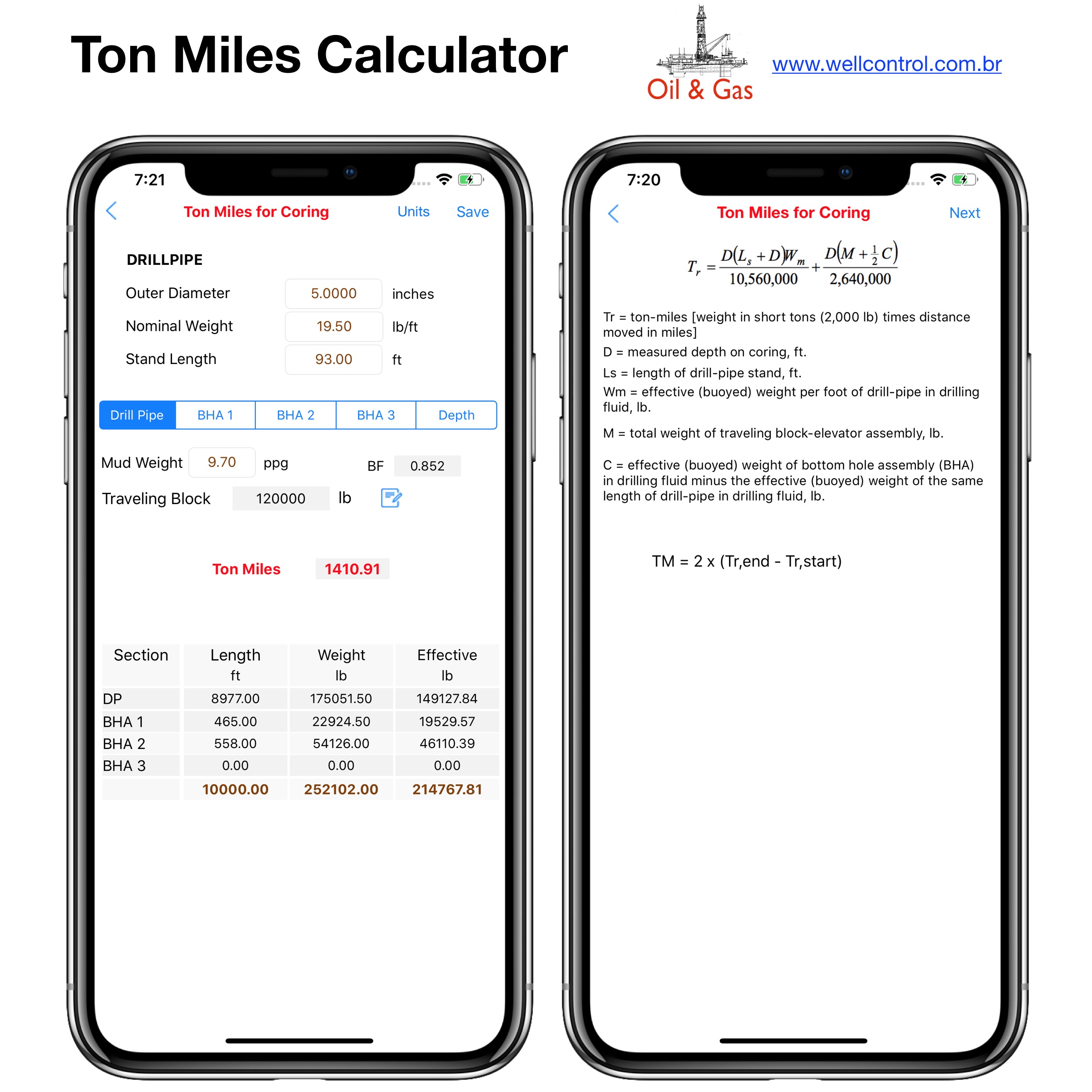
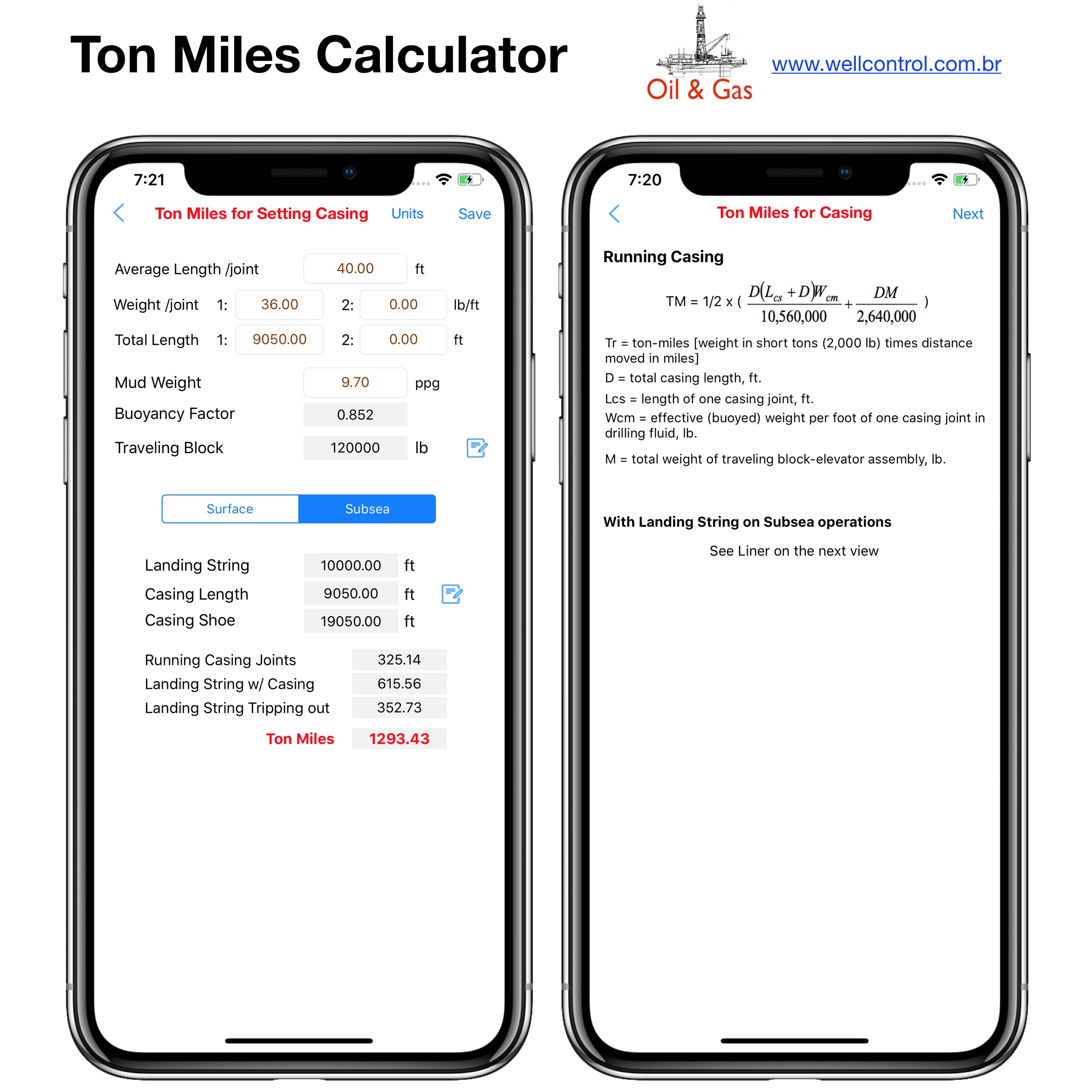
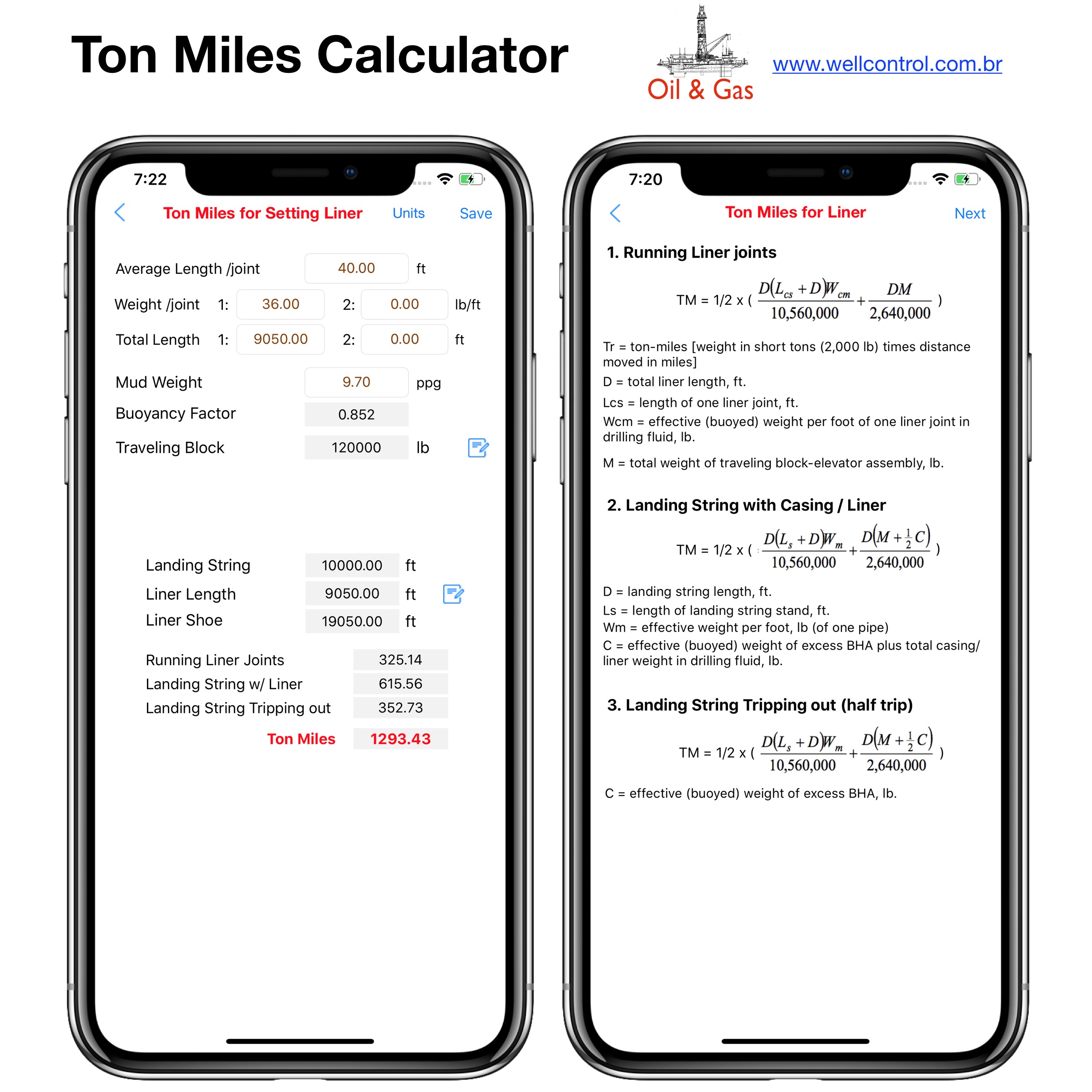
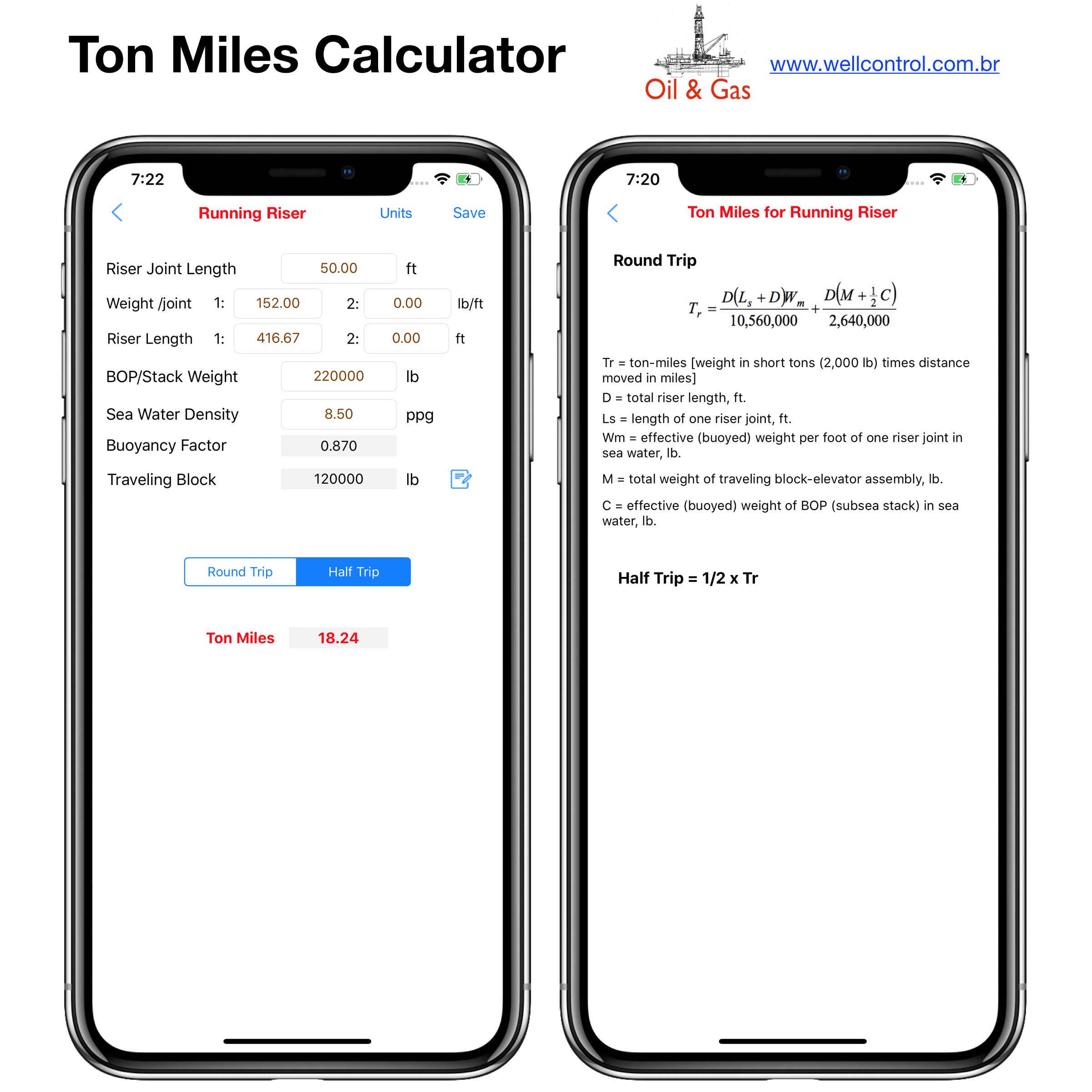
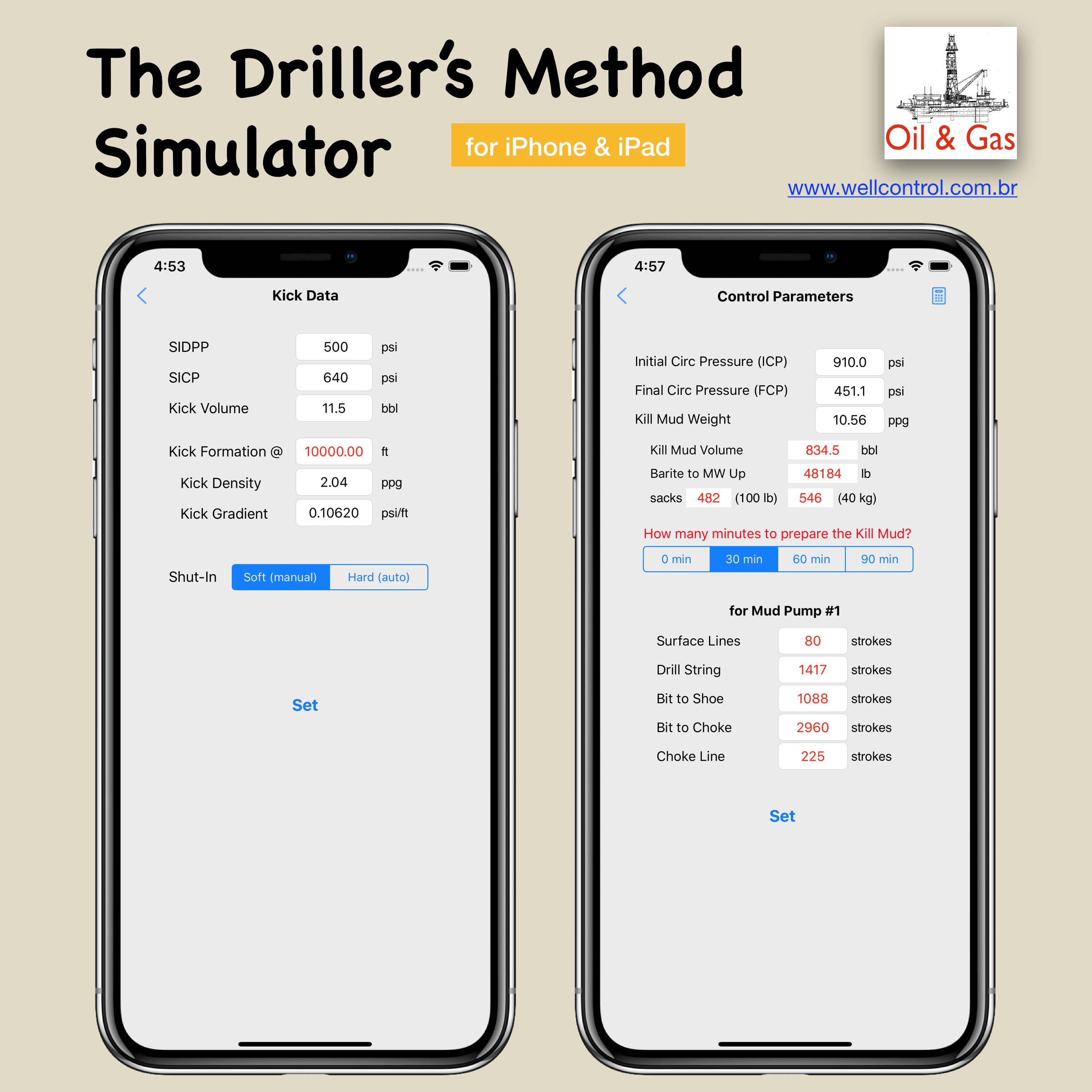
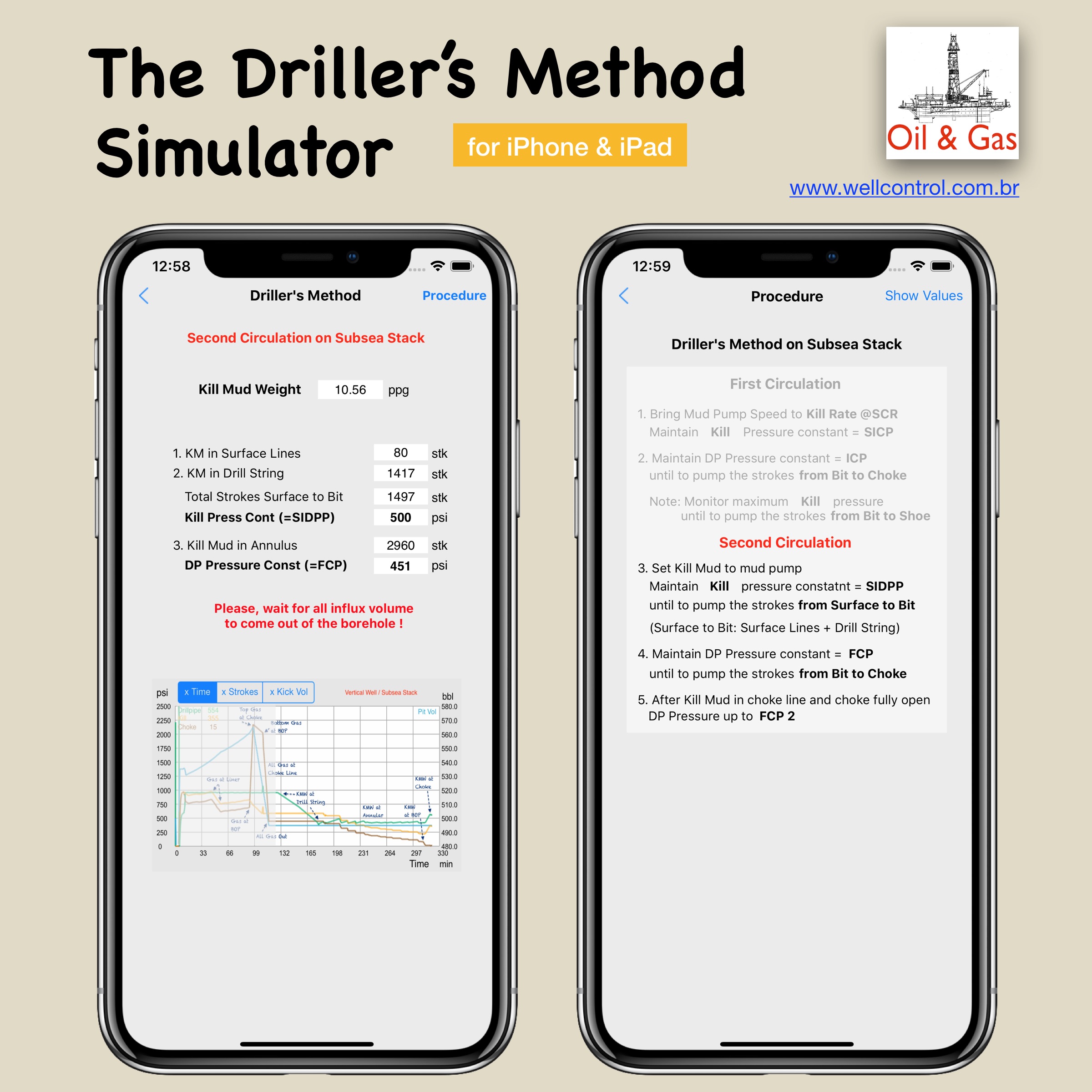
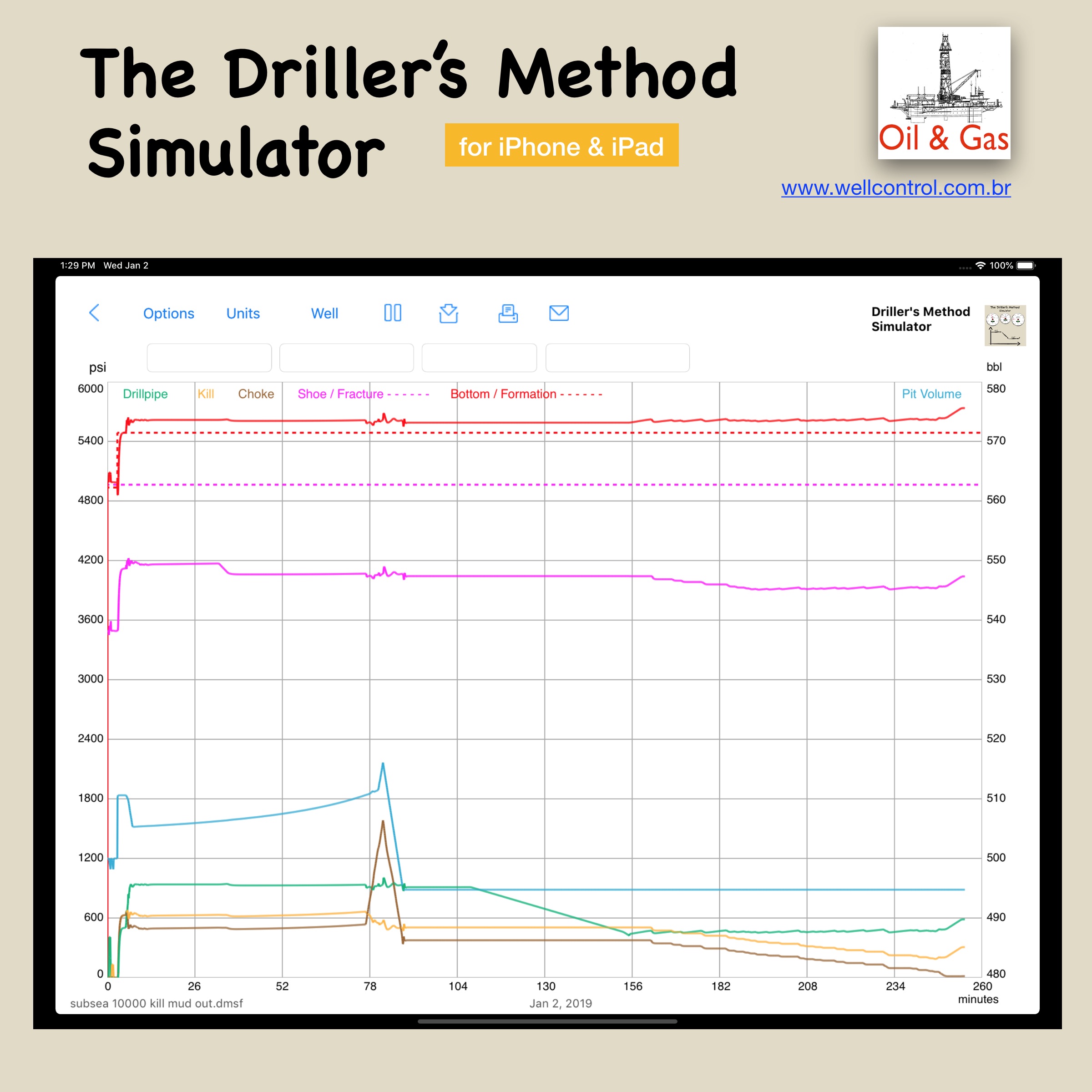
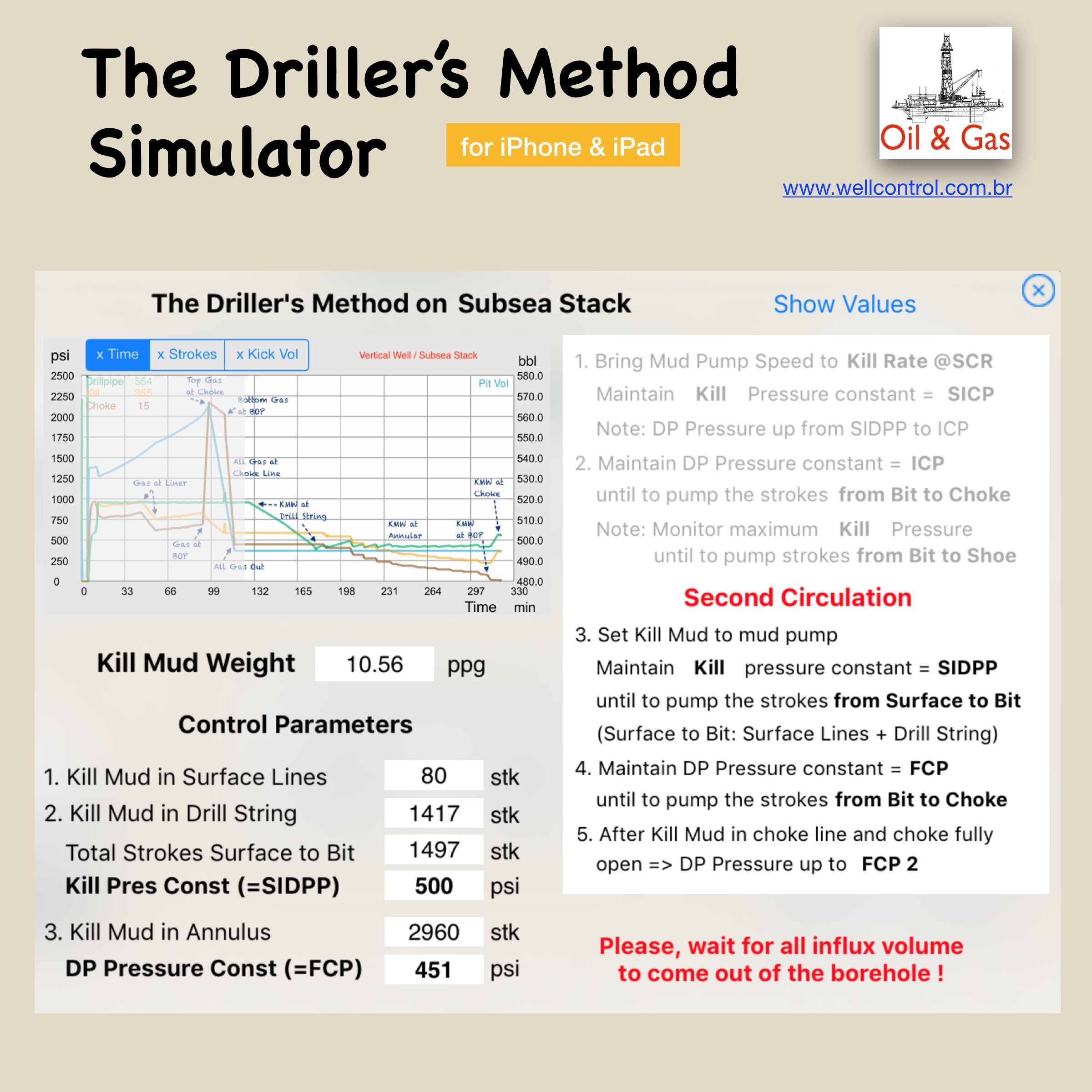
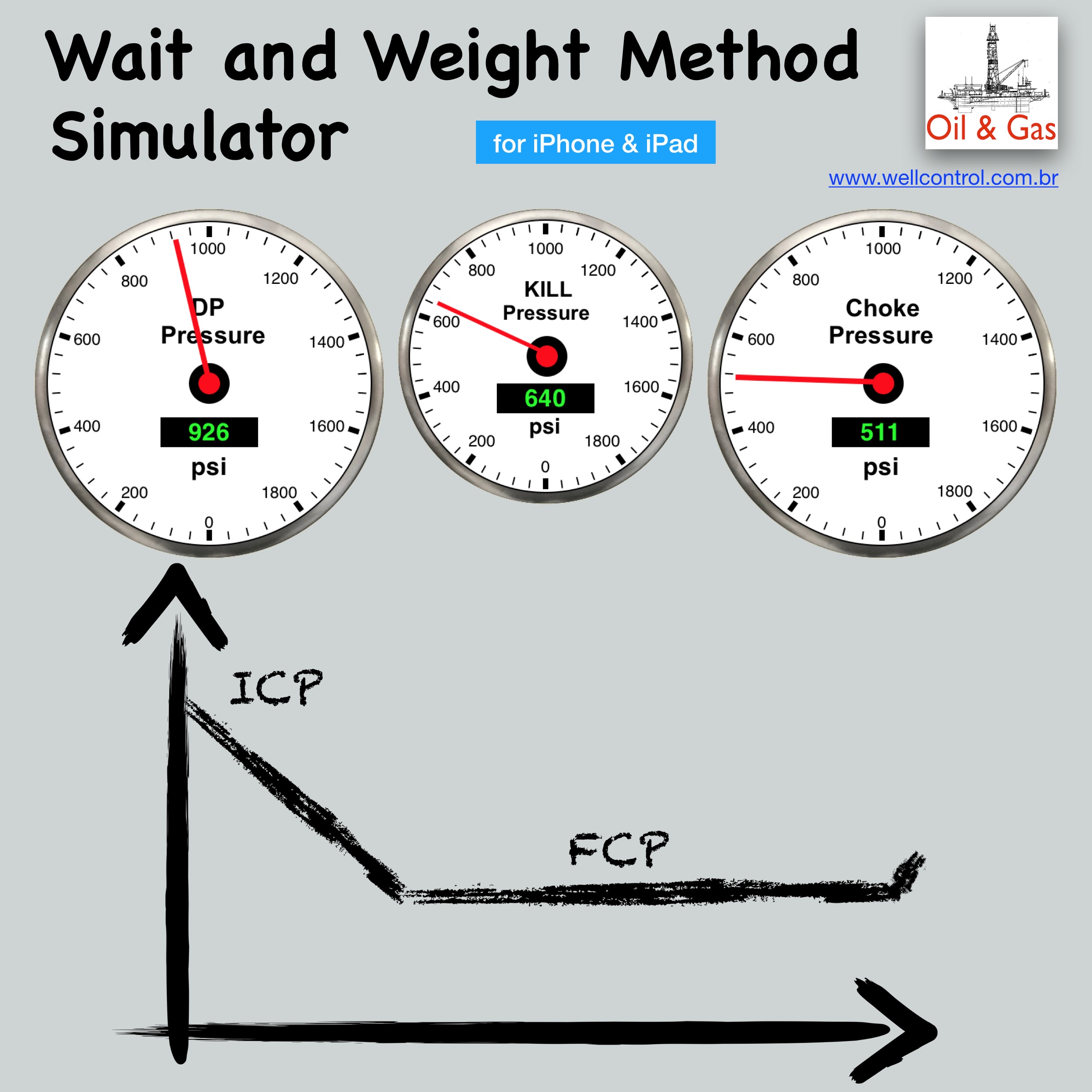
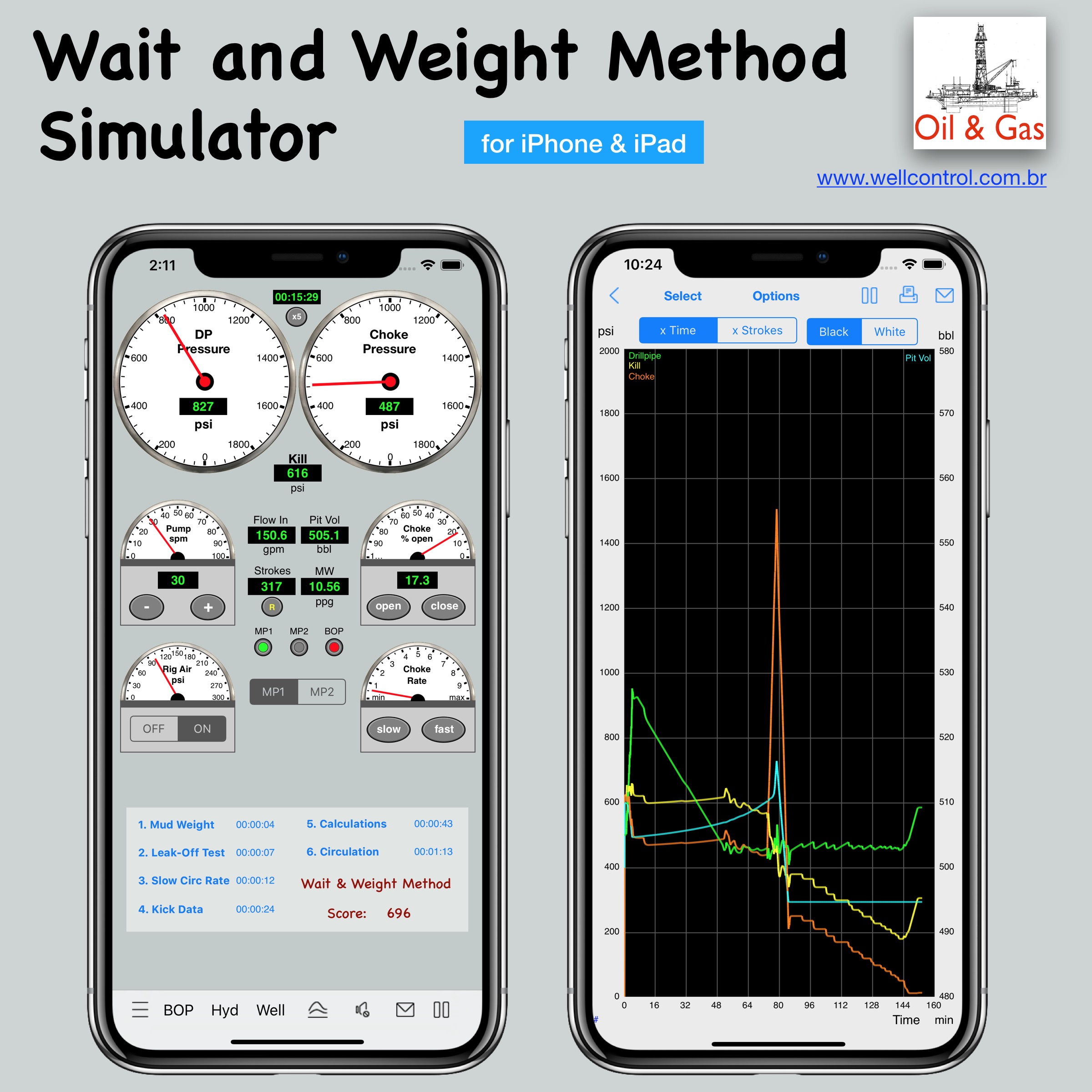
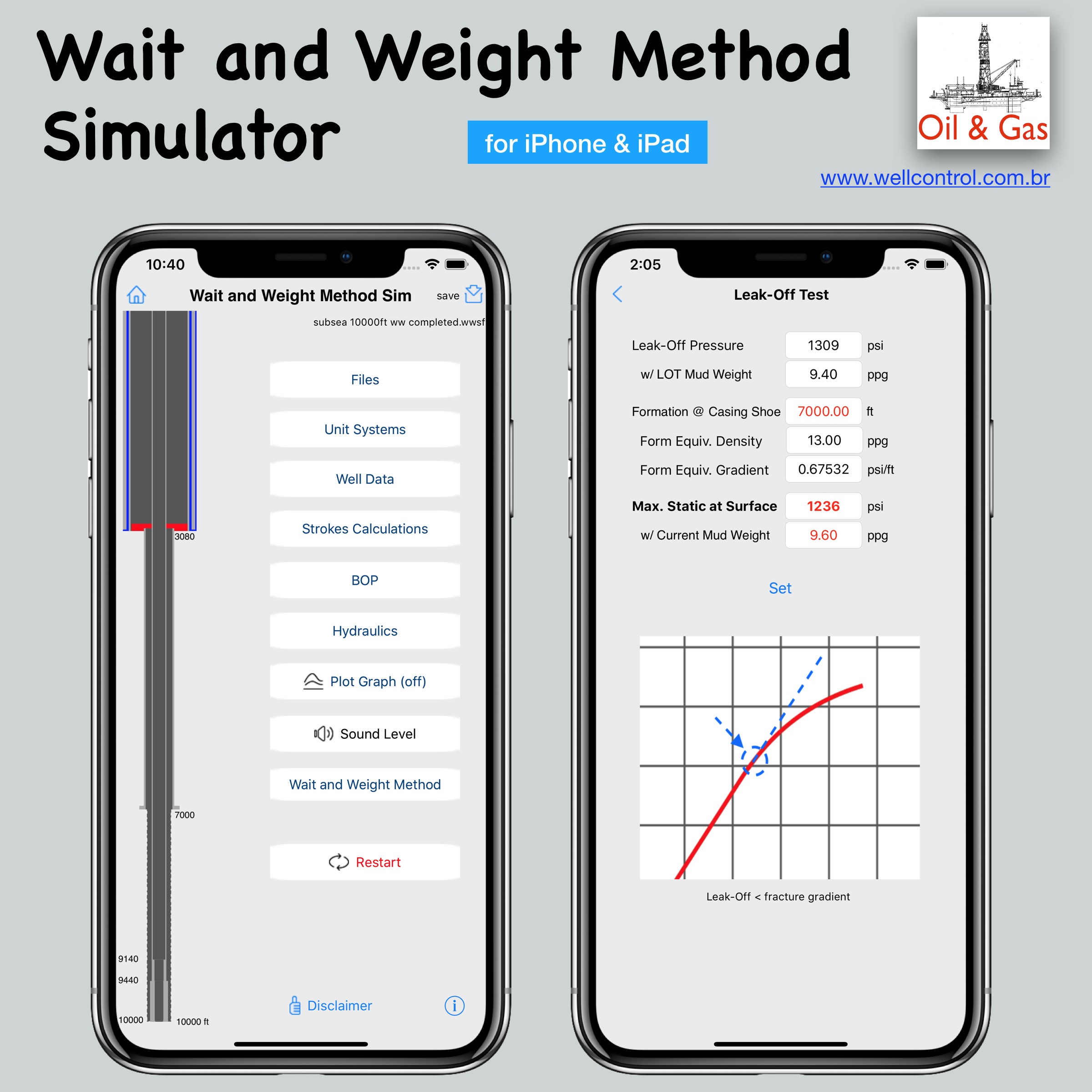
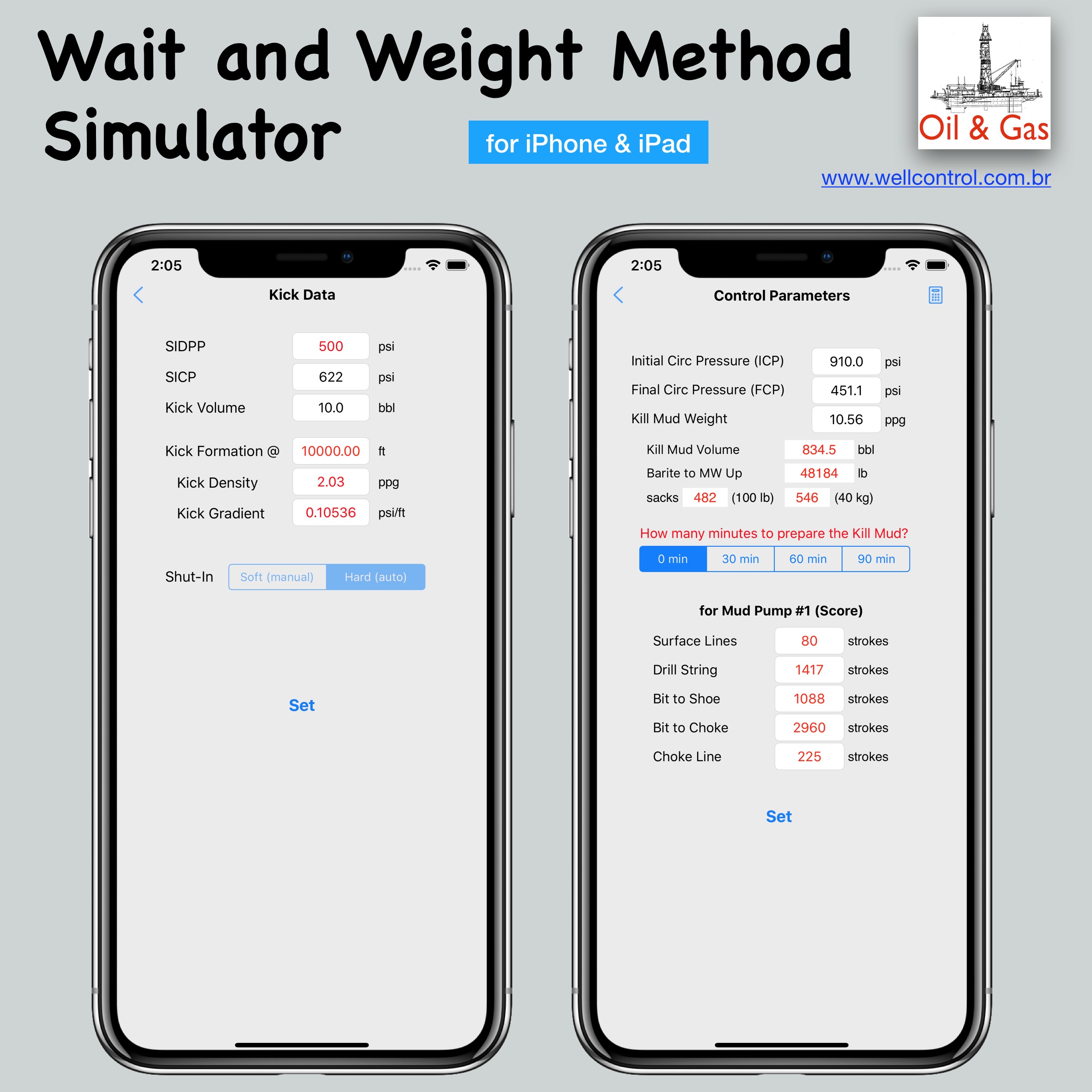
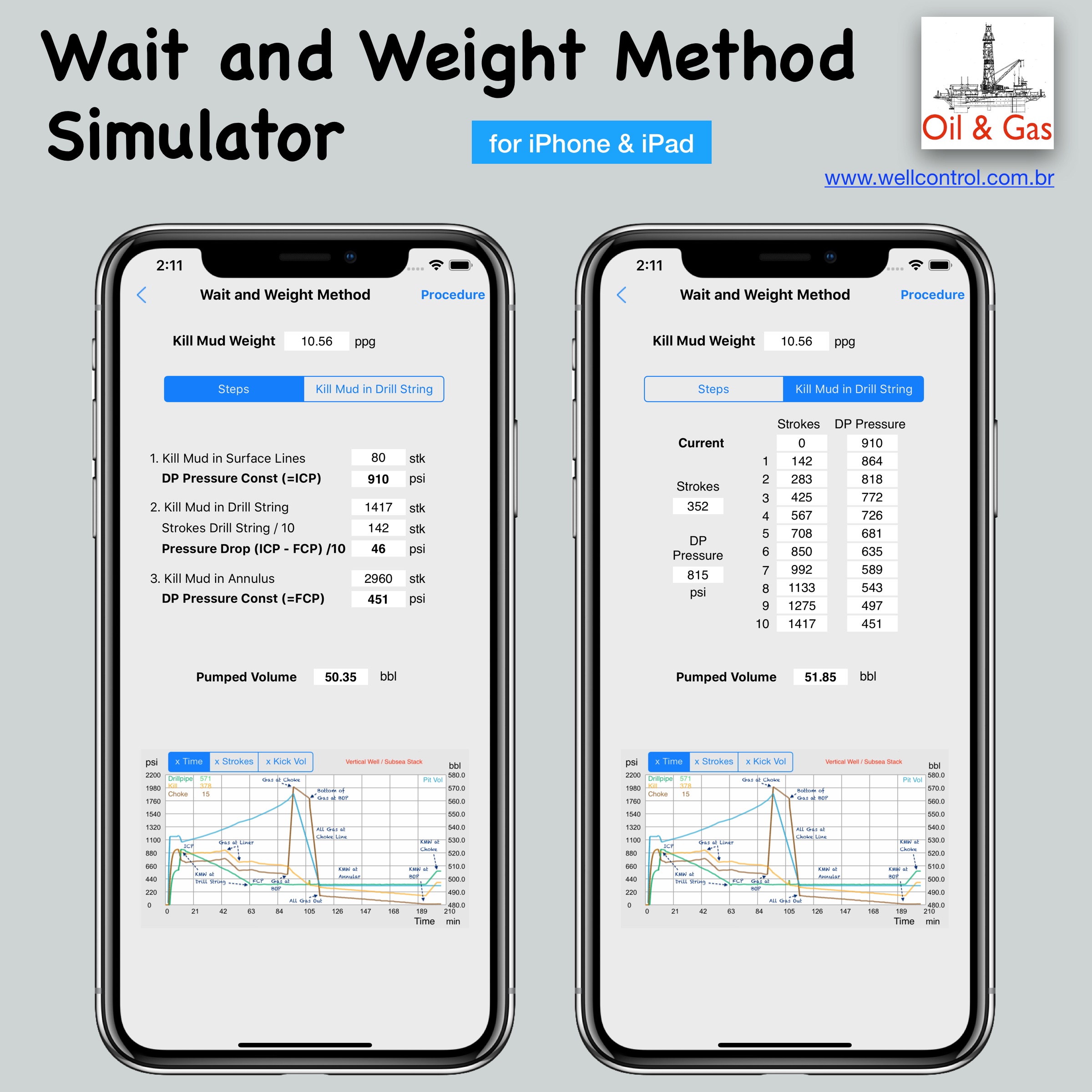
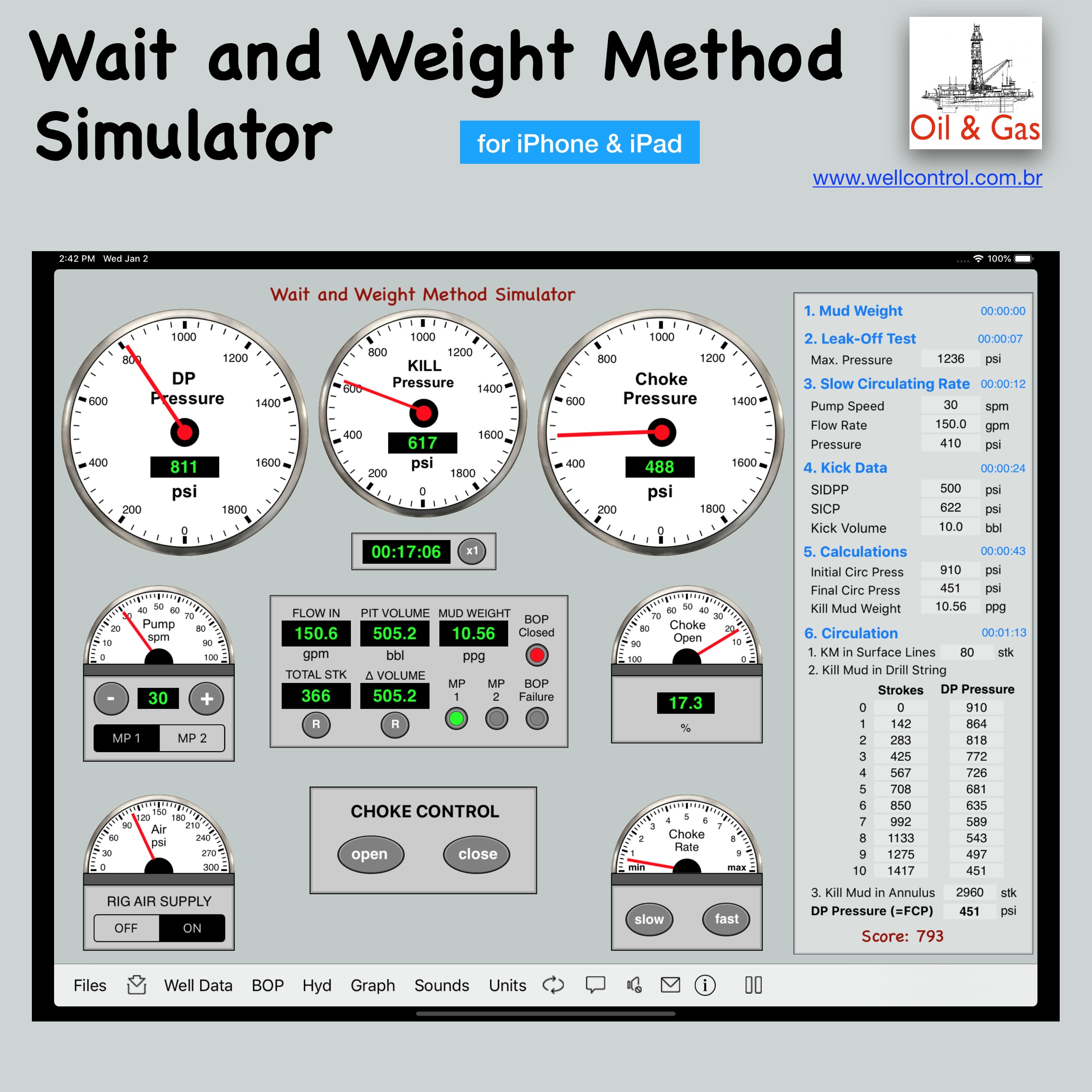
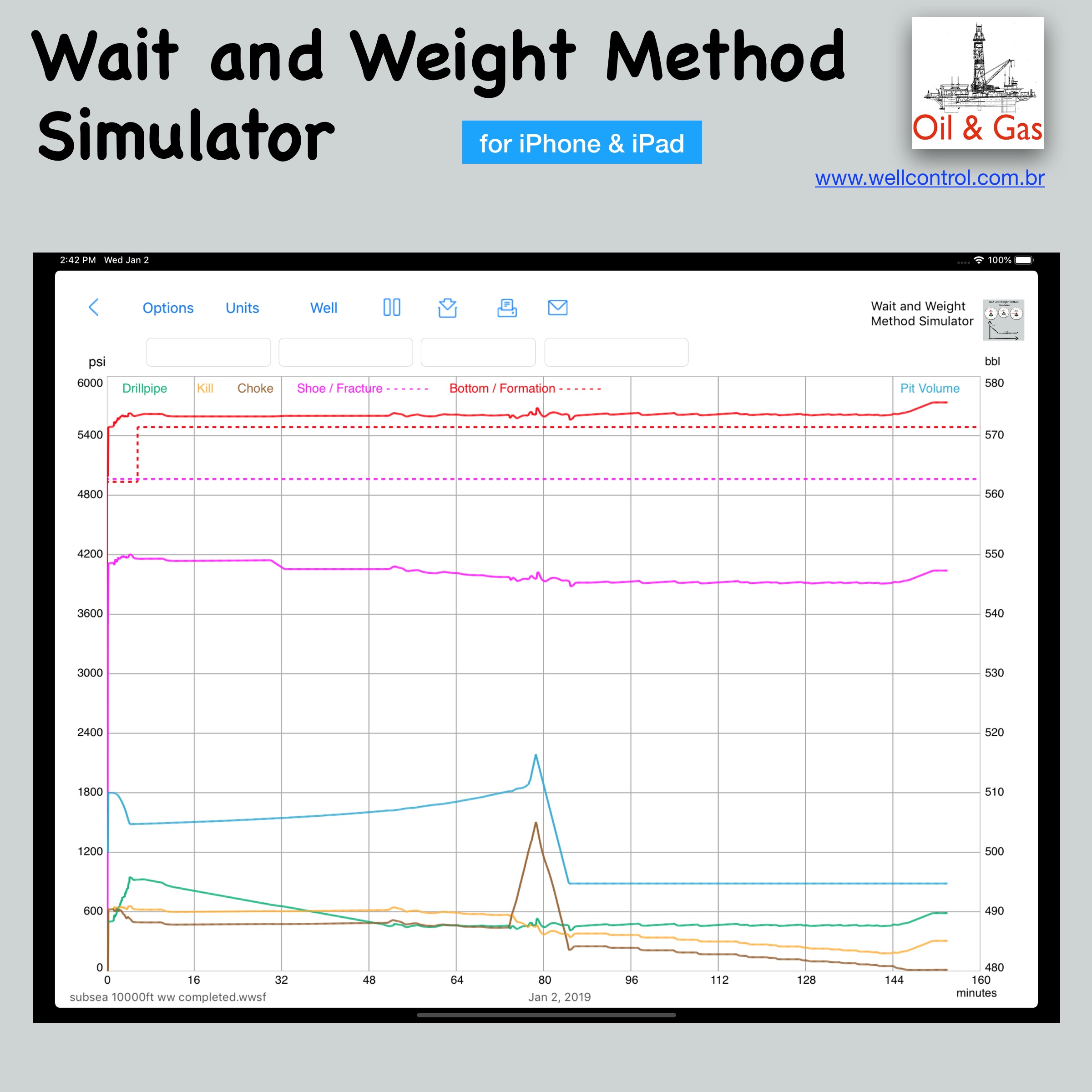
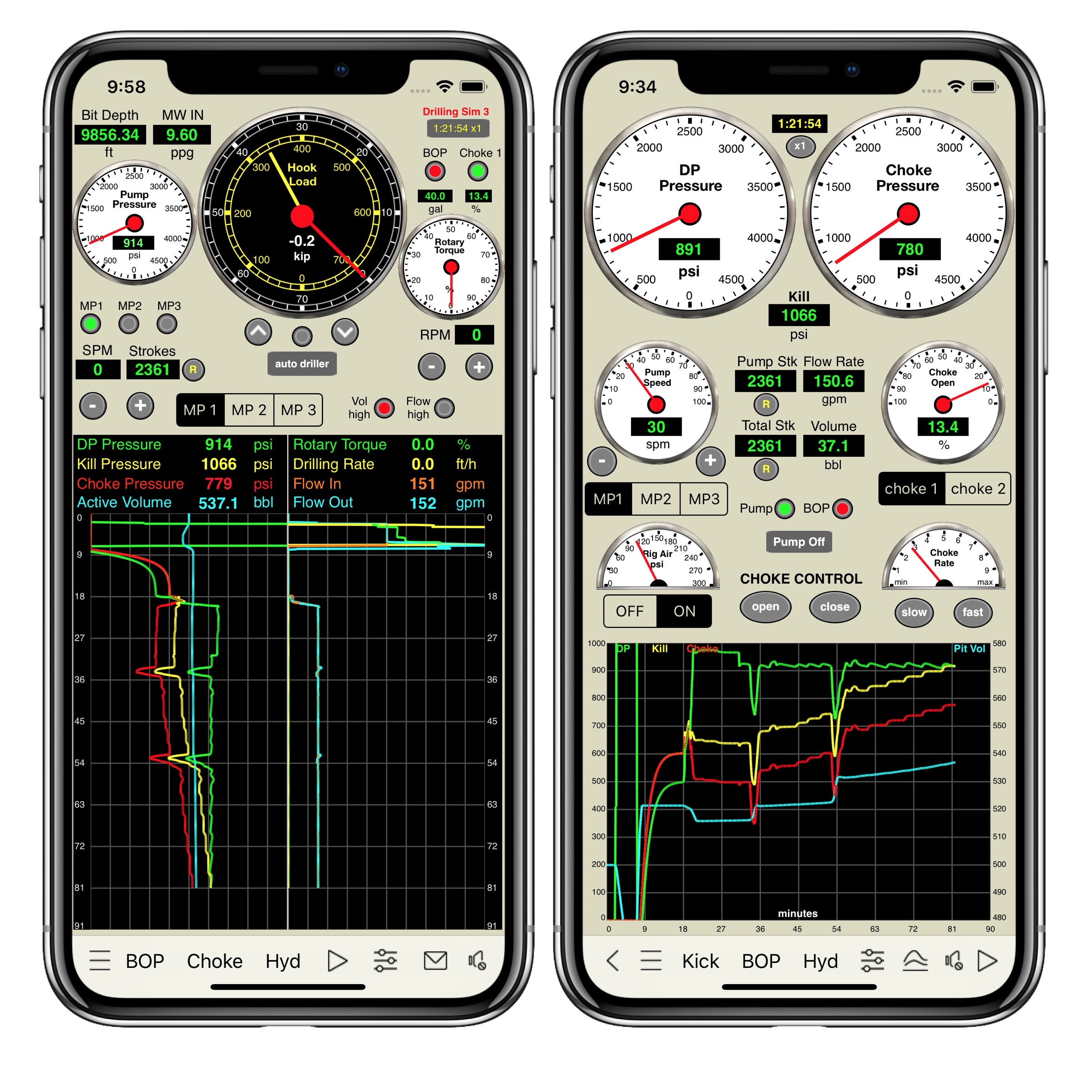
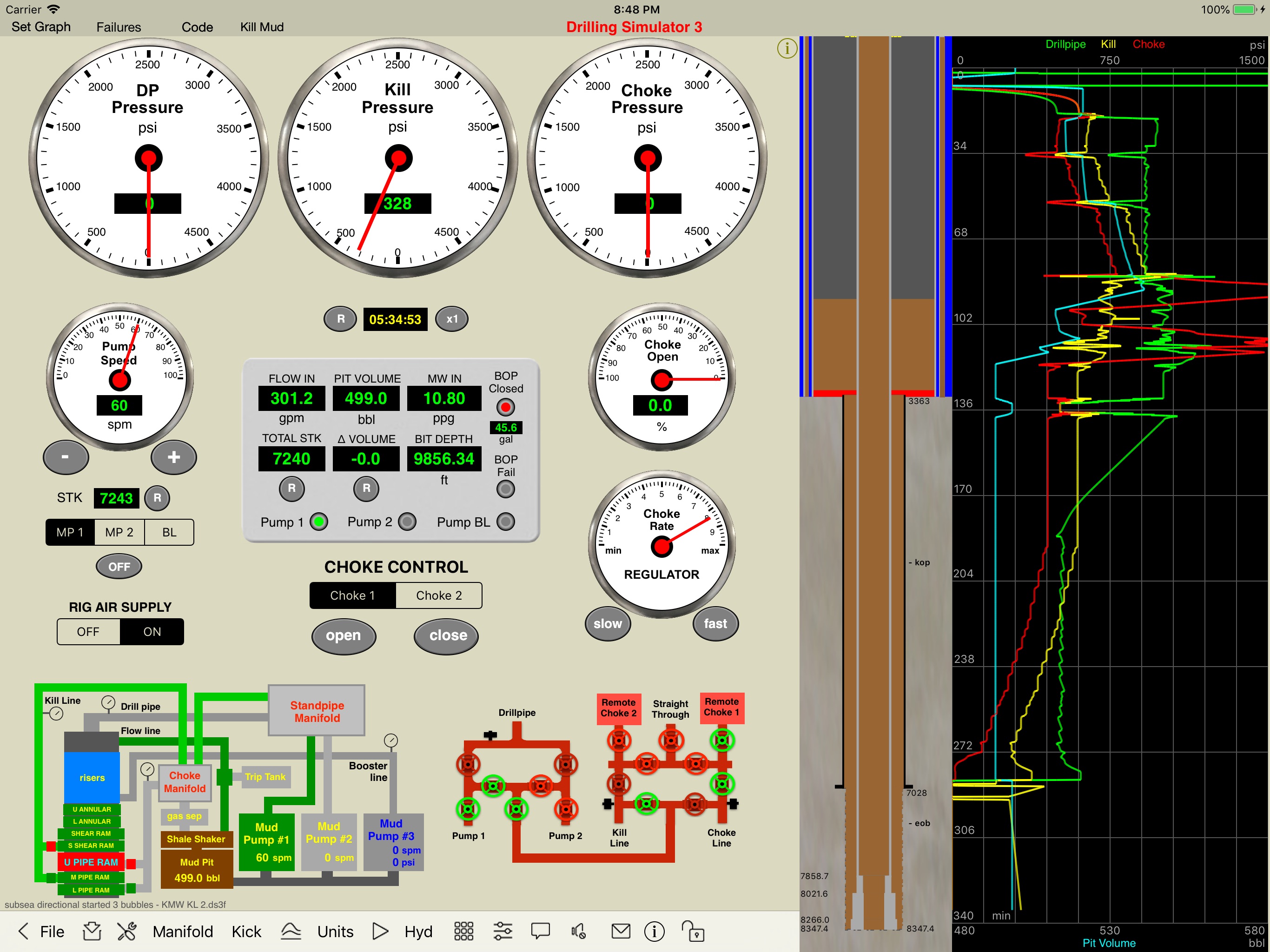
Screenshots
Please visit them by clicking on their respective links to see screenshots.
In our social networks there are many posts about Kick Tolerance.
DISCLAIMER
These tools & materials are provided ‘as is’ without warranties of any kind, express or implied.
Please verify the tools provided by this application by yourself before you use them. Ensure you understand the impact of using these tools.
Any use you choose to make of these tools & materials is undertaken by you entirely at you own risk.
Please visit our website for more details and other Oil & Gas Applications and for links to our profiles in social networks about well control.














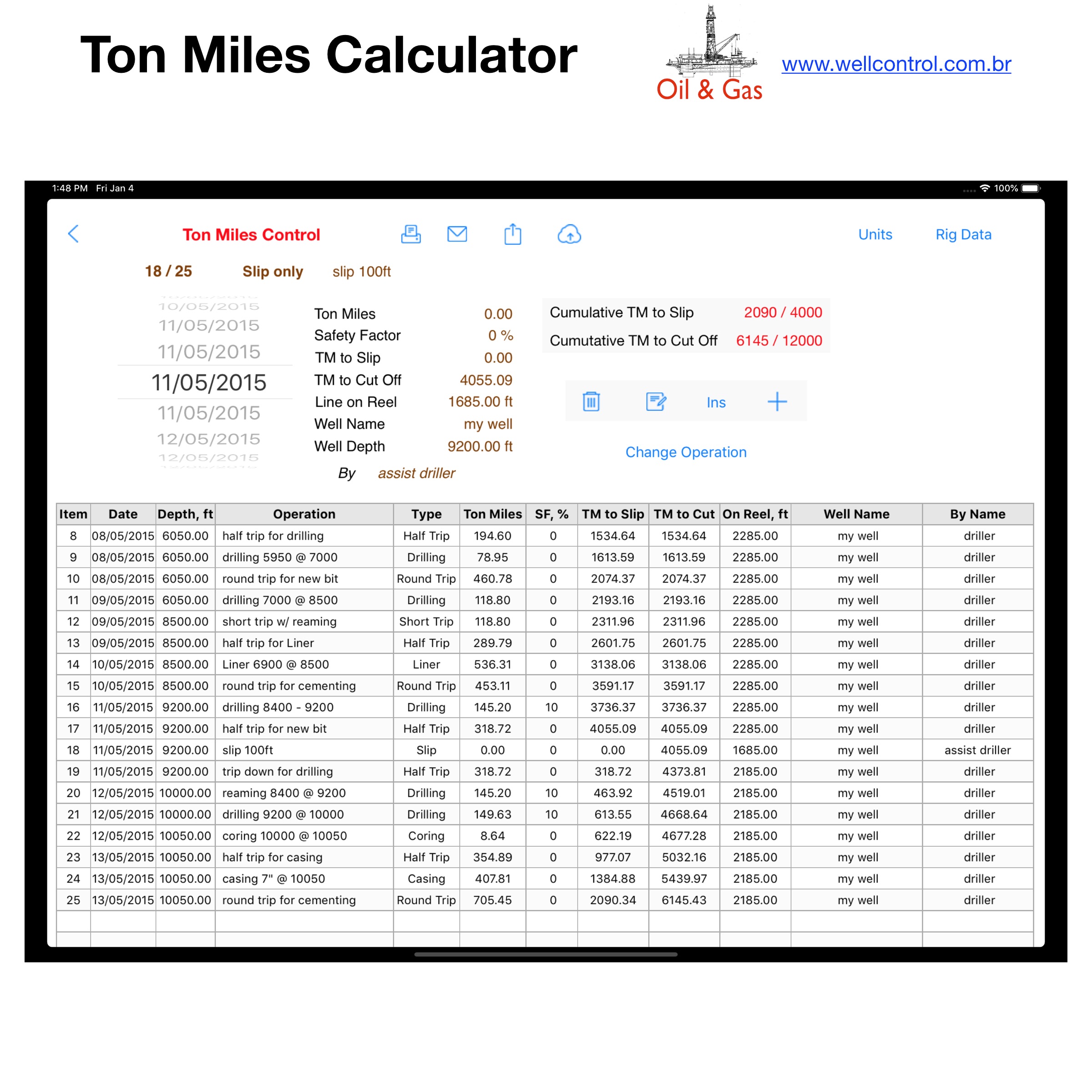
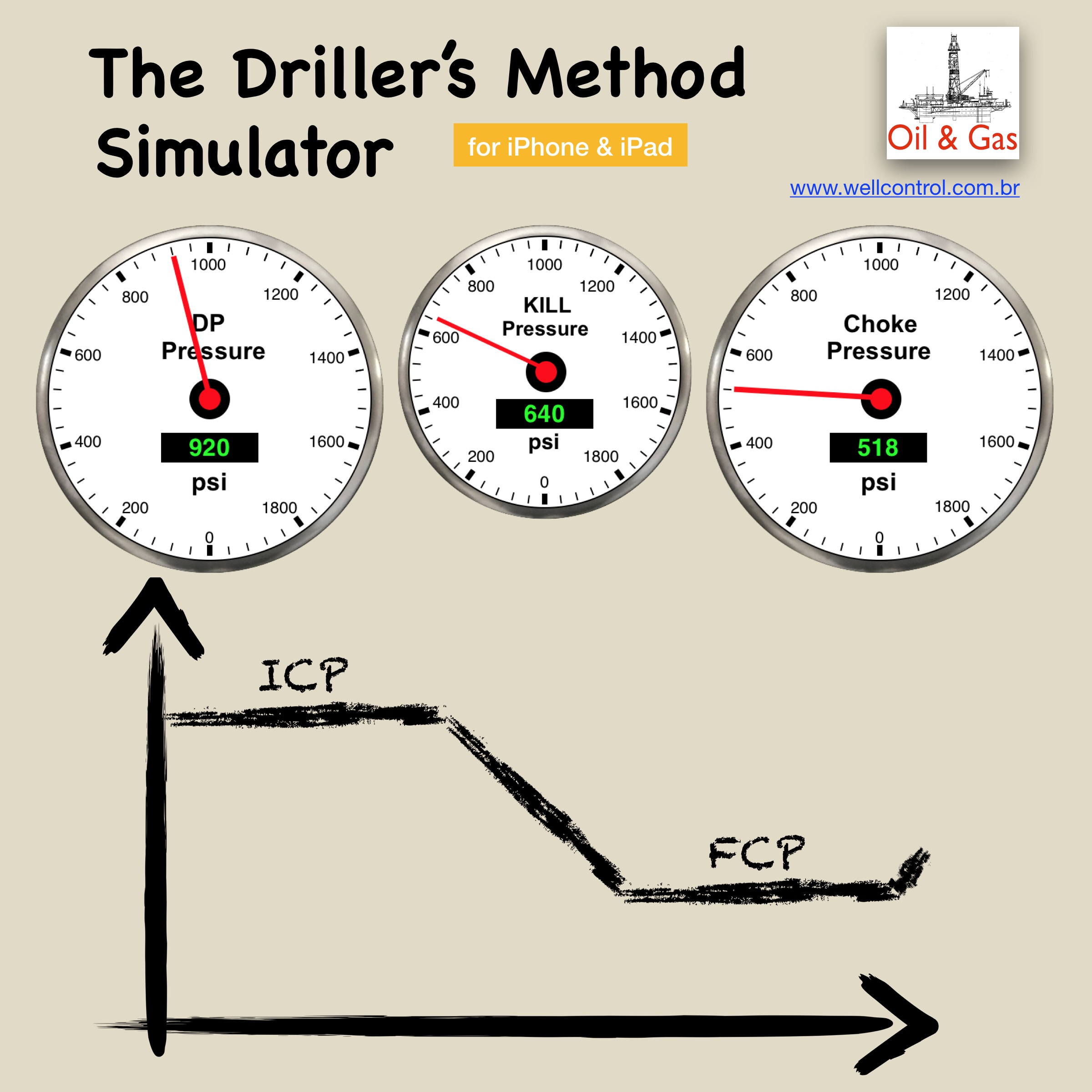
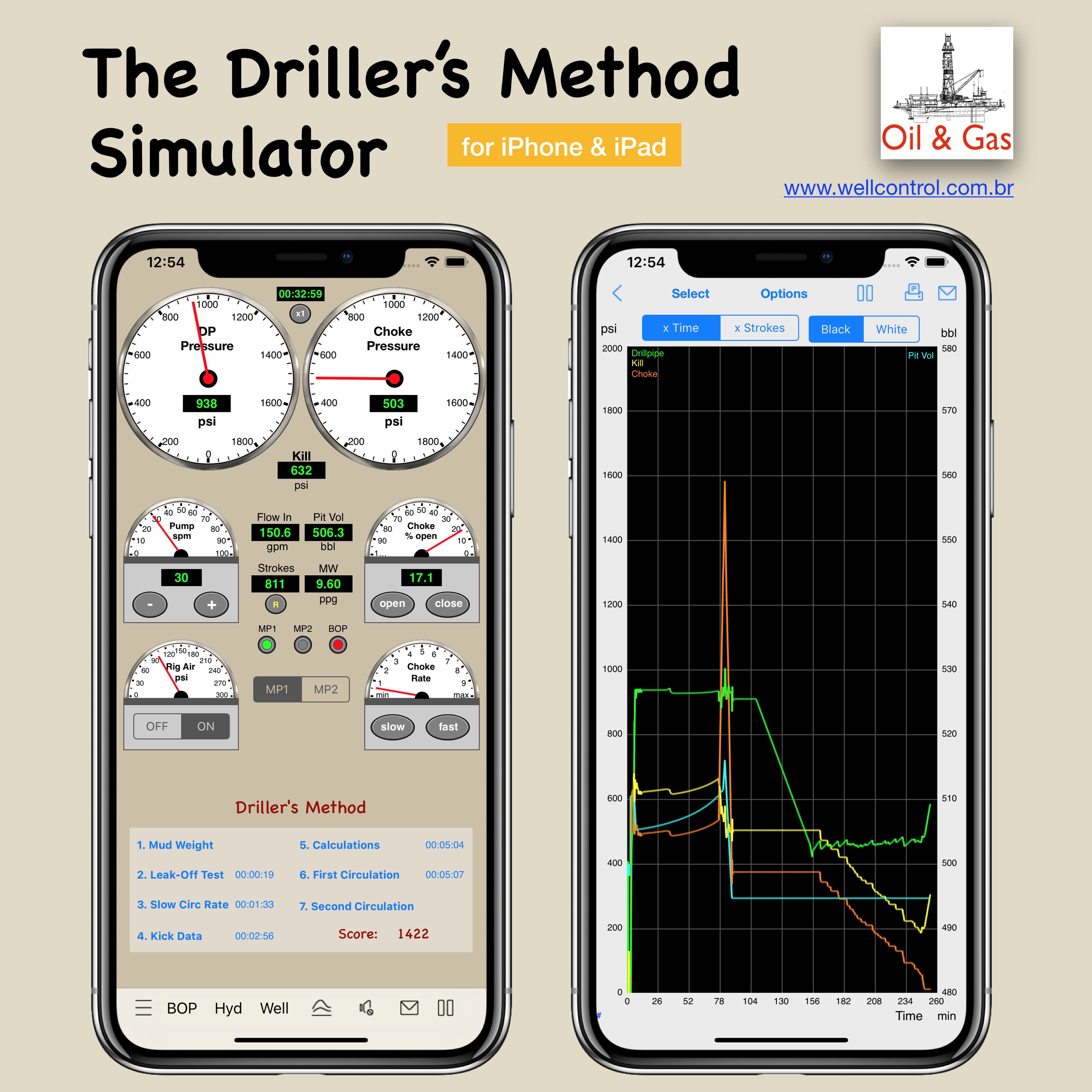
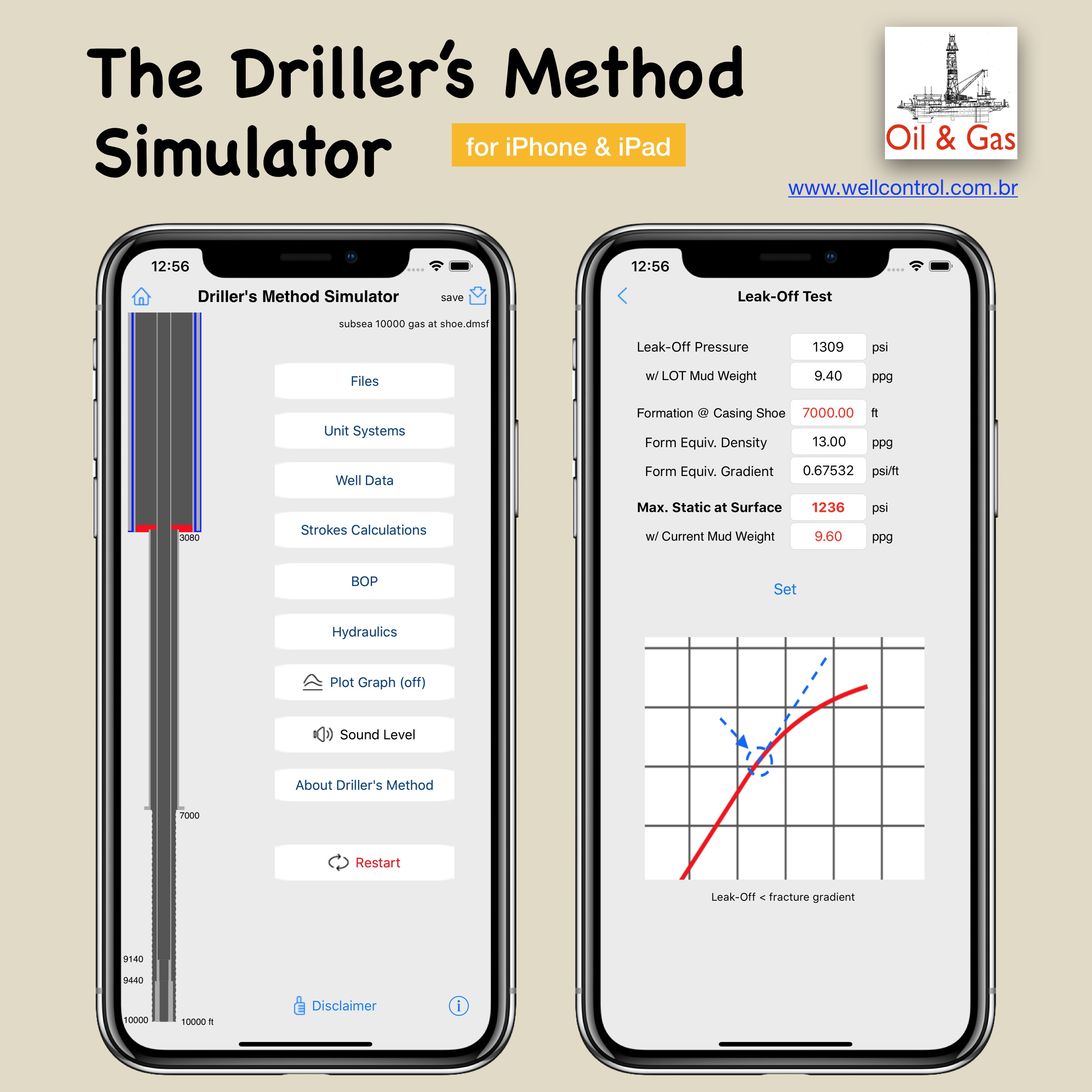












You must be logged in to post a comment.